Sommaire
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Étape 1 - Get PCBs for Your Projects Manufactured
- 3 Étape 2 - What is NB-IoT technology?
- 4 Étape 3 - Why NB-IoT?
- 5 Étape 4 - Barriers to NB-IoT
- 6 Étape 5 - NarrowBand-IoT in India
- 7 Étape 6 - Google Ping Test using nRF9160 DK and Airtel NB-IoT Service
- 8 Étape 7 - Received Response for the Ping
- 9 Étape 8 - nRf9160 AT Commands
- 10 Commentaires
Introduction
With the Internet of Things (IoT), everyday objects can now connect and exchange data. These smart objects are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to facilitate communication and data exchange with similar systems and devices over a network, typically the Internet.
By the end of 2025, it is estimated that there will be 38.6 billion IoT-connected devices worldwide. Managing such many devices necessitates a secure and reliable network to support them all. This is where the emerging technology of the Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) comes into play.
Matériaux
Hardware components:
Nordic Semiconductor nRF9160 Development Kit
Software apps and online services:
Nordic Semiconductor nRF Connect SDK
Outils
Étape 1 - Get PCBs for Your Projects Manufactured
You must check out PCBWAY for ordering PCBs online for cheap!
You get 10 good-quality PCBs manufactured and shipped to your doorstep for cheap. You will also get a discount on shipping on your first order. Upload your Gerber files onto PCBWAY to get them manufactured with good quality and quick turnaround time. PCBWay now could provide a complete product solution, from design to enclosure production. Check out their online Gerber viewer function. With reward points, you can get free stuff from their gift shop. Also, check out this useful blog on PCBWay Plugin for KiCad from here. Using this plugin, you can directly order PCBs in just one click after completing your design in KiCad.
Étape 2 - What is NB-IoT technology?
Narrowband IoT, abbreviated as NB-IoT, or LTE-M2, is a novel wireless technology that deviates from the standard licensed LTE framework. It is an LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) technology operating independently in previously unused 200-kHz bands, initially allocated for Global Systems for Mobile Communications networks (GSM).
In 2016, telecommunications giants such as Huawei, Ericsson, Qualcomm, and Vodafone collaborated to designate NB-IoT as 5G technology. They collectively established this standard in conjunction with 3GPP. This emerging technology is being employed to enable a myriad of new IIoT (Industrial IoT) devices, encompassing applications like smart parking, wearables, utilities, and industrial solutions.
Étape 3 - Why NB-IoT?
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) enables multiple devices to transmit data even without standard mobile network coverage. The licensed frequency spectrum it utilizes does not interfere with other devices, ensuring more reliable data transfer. As a standards-based Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology, NB-IoT can cover expansive areas while consuming minimal energy.
NB-IoT enjoys support from major mobile equipment, module, and chipset manufacturers. It can coexist with 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks. Its simple infrastructure allows for faster and more straightforward implementation. Additionally, Narrowband IoT can leverage the security and privacy features inherent in mobile networks.
Advantages of NB-IoT
Power-Efficient and Cost-Effective – Narrowband-IoT exhibits low energy consumption while covering vast areas, connecting up to 50,000 devices per NB-IoT network cell. This enhances the power efficiency of user devices and contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness of the system. The minimal power consumption allows for a battery life exceeding ten years.
Secure and Reliable – Leveraging a licensed spectrum ensures greater reliability for users and guarantees resource allocation for managed Quality of Service (QoS). This results in less interference and more reliable transmissions. The underlying technology is straightforward to design, develop, and deploy. It incorporates security and privacy features comparable to LTE mobile networks, supporting user identity confidentiality, data integrity, entity authentication, and mobile equipment identification.
Wider Deployment and Global Reach – Narrowband-IoT, with lower bit rates than LTE-M1, can directly connect sensors to the base station without requiring a gateway for connectivity. This characteristic makes it an excellent option for extensive deployment at lower costs. NB-IoT is capable of functioning in deep underground and enclosed spaces. Utilizing a mobile wireless network enhances scalability, providing a broader global reach.
Étape 4 - Barriers to NB-IoT
Easy deployment and good range are just a few of the advantages of NB-IoT. However, as with all technology, NB-IoT also comes with a few limitations, including the following:
- The data rate is low compared to LTE cat-M1.
- NB-IoT is considered ideal for idle devices.
- No support for VoLTE (Voice Over LTE) for speech transmission means no voice transmission.
- Roaming, though expected soon, is not supported yet.
- With LTE support finding favor with carriers, deployment could be a problem.
- Increased initial costs.
Étape 5 - NarrowBand-IoT in India
In India, the predominant practice among mobile operators is to utilize the 900 MHz licensed band for NB-IoT operations. Major players in the Indian Telecom sector have already highlighted the potential use cases for NB-IoT deployment. They frequently emphasize the benefits that businesses and the government can derive from adopting this technology, particularly in the pursuit of Smart Cities.
NB-IoT in India holds promise for various applications within a smart city context, ranging from air-quality monitoring and smart parking to damage prediction in the event of a disaster and waste management. Several countries have already initiated the deployment of such solutions and are actively seeking ways to enhance and expand them. NB-IoT has the potential to emerge as a mainstream technological resource in India, positioning the country among the leading global technology innovators.
In India, two major telecom service providers, Reliance Jio and Airtel, have introduced NB-IoT services. However, these services are not commercially available for individual users, unlike in other countries where single users can access such services.
To utilize NB-IoT services in India, users are required to make purchases through registered firms in large quantities. I obtained this information through interactions with the respective company sales teams. In my attempts to gather technical details, I engaged with Jio and Airtel over several months, holding a series of regular meetings. Unfortunately, Jio repeatedly denied my requests and did not provide basic information regarding the technical aspects. This experience left me dissatisfied with the Reliance Jio NB-IoT sales team.
Airtel NB-IoT provided us with the opportunity to conduct basic functionality tests of NB-IoT in their IoT lab. My objective was to assess how NB-IoT works in India. I requested a set of tests to evaluate the performance of NB-IoT connectivity. Before testing NB-IoT in India, I conducted tests on NB-IoT technology in the USA remotely, with the assistance of my friends. For the USA tests, I utilized the nRF Thingy 91 and Arkessa SIM. These tests were successful, and I was able to integrate them with Edge Impulse.
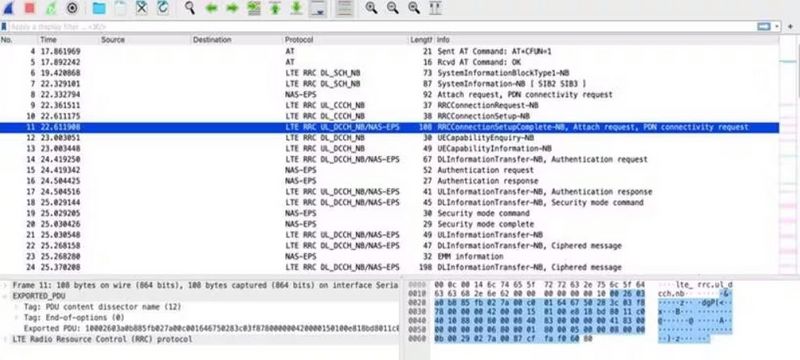
Upon returning to India, we tested NB-IoT connectivity using the nRF9160 Development Kit with an Airtel NB-IoT SIM. During this period, I had the opportunity to discuss the NB-IoT test details with Gaurav Kapoor and his team from Nordic Semiconductor. They provided valuable assistance in testing the nRF9160.
The nRF9160 was tested at the Airtel Manesar lab, where a straightforward Ping test was conducted using nRF9160 AT commands. The test utilized firmware versions nRF9160_1.3.4 and nRF Connect SDK v2.3.0. Airtel also has an IoT lab in Bengaluru, where NB-IoT-related tests can be conducted. To access the lab, prior permission must be obtained from the respective teams.
Étape 6 - Google Ping Test using nRF9160 DK and Airtel NB-IoT Service
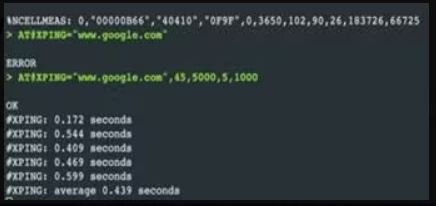
Conducted a Google Ping test utilizing the nRF9160 Development Kit and Airtel's NB-IoT service. The test involved sending Ping requests to Google servers to assess the round-trip time for responses. The nRF9160 DK, coupled with Airtel's NB-IoT service, served as the platform for evaluating the connectivity and performance of the NB-IoT network in this specific test.
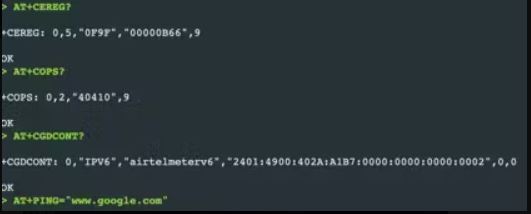
Step 1: Check the current network registration status of the nRF9160 modem.
AT+CEREG=?
- This command is Essential for determining if the device is connected to the cellular network and able to send and receive data.
Step 2: Searches for available cellular networks in the surrounding area.
AT+COPS=?
Step 3: Verify the configuration of Packet Data Protocol (PDP) contexts, which are essential for establishing data connections over a cellular network.
AT+CGDCONT?
It retrieves information like the Access Point Name (APN), PDP type, and other parameters for each defined context.
Step 4: Initiate a ping operation to test connectivity to a specified IP address or hostname.
AT+PING = "www.google.com",45,5000,5,1000
Syntax: AT+PING=<destination_IP_or_hostname>,<packet_size>,<timeout>,<count>,<interval>
- destination_IP_or_hostname: The IP address or hostname to ping (in this case, "www.google.com")
- packet_size: The size of the ping packets in bytes (45 bytes in this example)
- timeout: The maximum time to wait for a response in milliseconds (5000 ms in this example)
- count: The number of ping packets to send (5 in this example)
- interval: The time interval between sending ping packets in milliseconds (1000 ms in this example)
Étape 8 - nRf9160 AT Commands
Follow the link provided, to know AT Commands in detail.
https://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/pdf/nrf9160_at_commands_v2.2.pdf
Note: NB-IoT is not deployed in all states of India
Published



 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português