Sommaire
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Étape 1 - What Is Home Assistant?
- 3 Étape 2 - Get PCBs for Your Projects Manufactured
- 4 Étape 3 - Installation Steps:
- 5 Étape 4 - Create a Virtual Machine in VirtualBox:
- 6 Étape 5 - Load the Home Assistant Image:
- 7 Étape 6 - Configure the VM:
- 8 Étape 7 - Install Home Assistant:
- 9 Étape 8 - Onboarding:
- 10 Étape 9 - Important Notes:
- 11 Commentaires
Introduction
Matériaux
Outils
Étape 1 - What Is Home Assistant?
Home Assistant is an open-source home automation platform that acts as the central hub for managing your smart home. Here are some key features:
Integration with Over 1000 Brands:
Home Assistant plays well with a vast array of devices and services. From smart lights and thermostats to security cameras and voice assistants, it integrates seamlessly.
Once you set up your devices, Home Assistant automatically scans your network and allows you to configure them easily.
Powerful Automation:
Imagine your home working for you! With Home Assistant’s advanced automation engine, you can create custom rules and triggers.Examples:
Turn on the lights when the sun sets.
Extendable with Add-Ons: Home Assistant isn’t limited to its core functionality. You can easily install additional applications (add-ons) to enhance your setup.Receive an alert if you accidentally leave the garage door open.
Examples:
Run AdGuard for DNS-based ad blocking.
Use NodeRed for third-party automation.
Local Data Privacy:Turn Home Assistant into a Spotify Connect target.
Unlike cloud-based solutions, Home Assistant keeps your data local. It communicates directly with your devices without relying on external servers.
Your privacy is preserved, and no data is stored in the cloud.
Companion Mobile Apps:
Control your devices and receive notifications using the official Home Assistant apps. These apps also enable presence detection, allowing you to trigger automation based on your location. Rest assured, your data is sent directly to your home, with no third-party access.
Installation Options:
Home Assistant OS: A ready-to-use image for devices like Raspberry Pi, Odroid, or Intel NUC.
Home Assistant Supervised: Install Home Assistant on a generic Linux system using Docker.
Home Assistant Container: Run Home Assistant in a Docker container.
Home Assistant Core: For advanced users who prefer manual installation on Python environments.
By setting it up in a virtual machine, you can experiment with Home Assistant without affecting your primary Windows environment.
Prerequisites:
- Windows 11: Ensure you’re running Windows 11 on your host machine.
- VirtualBox: Download and install VirtualBox if you haven’t already.
Étape 2 - Get PCBs for Your Projects Manufactured
You must check out PCBWAY for ordering PCBs online for cheap!
You get 10 good-quality PCBs manufactured and shipped to your doorstep for cheap. You will also get a discount on shipping on your first order. Upload your Gerber files onto PCBWAY to get them manufactured with good quality and quick turnaround time. PCBWay now could provide a complete product solution, from design to enclosure production. Check out their online Gerber viewer function. With reward points, you can get free stuff from their gift shop. Also, check out this useful blog on PCBWay Plugin for KiCad from here. Using this plugin, you can directly order PCBs in just one click after completing your design in KiCad.
Étape 3 - Installation Steps:
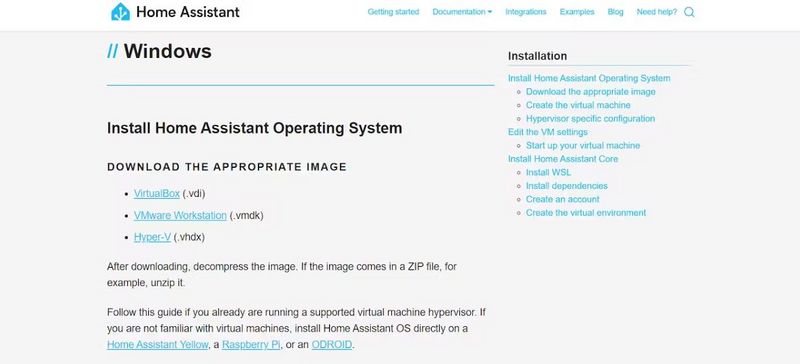
Download the Home Assistant Image:
- Visit the Home Assistant installation page.
- Under the “As a virtual appliance (x86_64/UEFI)” section, download the VirtualBox Disk Image (VDI) file. This image contains everything needed to run Home Assistant on Windows.
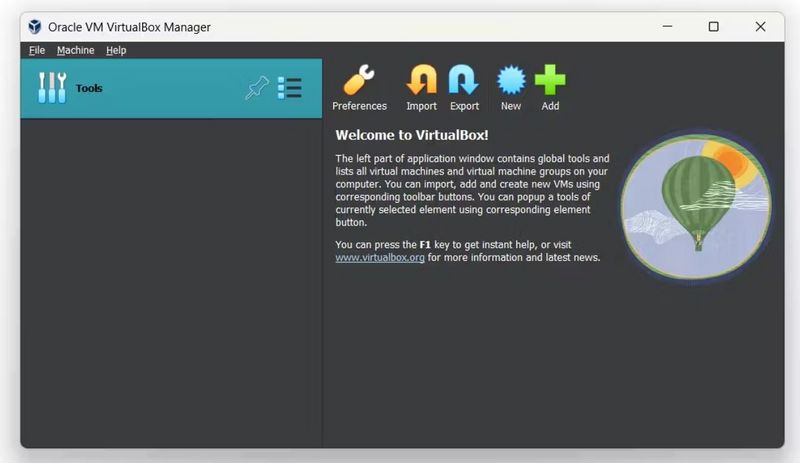
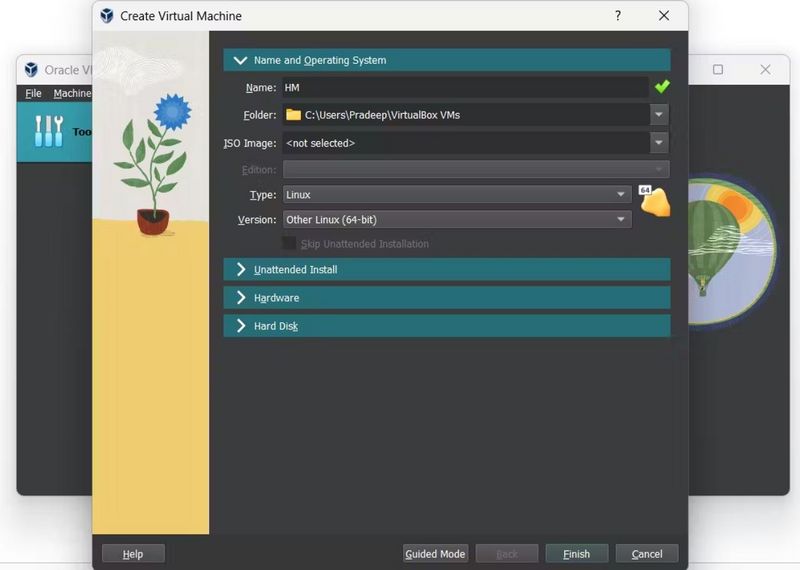
Étape 4 - Create a Virtual Machine in VirtualBox:
- Open VirtualBox and click on “New” to create a new virtual machine.
- Choose a name for your VM (e.g., “HomeAssistant”).
- Select “Linux” as the type and “Other Linux (64-bit)” as the version.
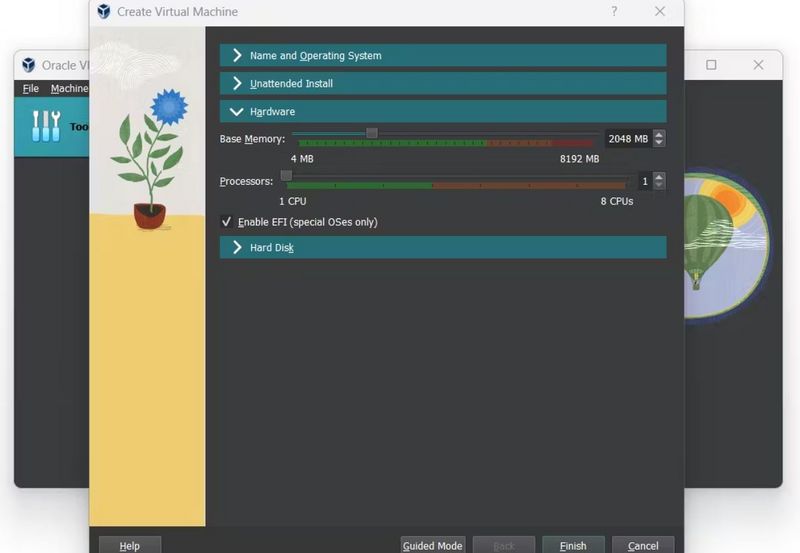
- Allocate at least 2 GB of RAM, 32 GB of storage, and 2 vCPUs to the VM. Adjust these resources based on your needs.
Étape 5 - Load the Home Assistant Image:
- In the VM settings, go to the “Harddisk” tab.
- Add a new optical drive and select the Home Assistant VDI file you downloaded.
- Make sure the optical drive is set as the first boot device.
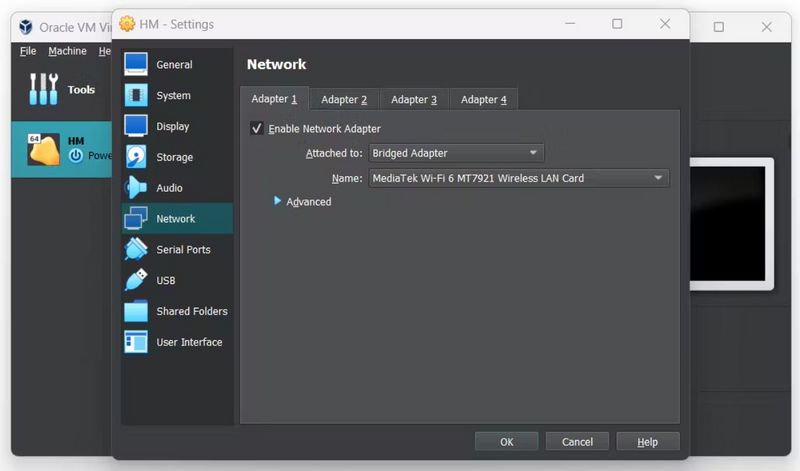
Étape 6 - Configure the VM:
- Go to the “Network” tab and ensure that the network adapter is set to “Attached to Bridged Adapter.” This allows Home Assistant to communicate with other devices on your network.
- Save the settings and start the VM.
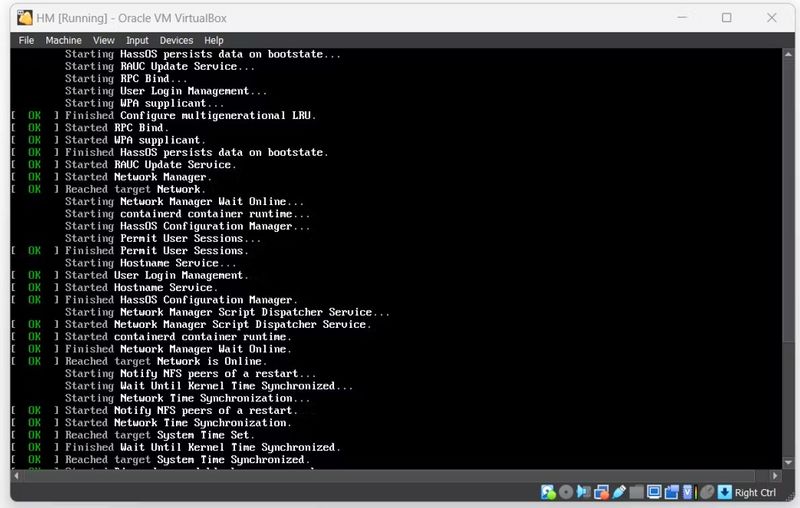
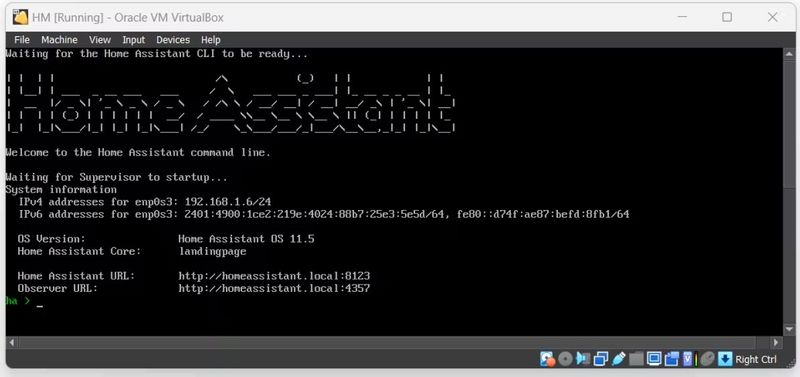
Étape 7 - Install Home Assistant:
- Observe the boot process of the Home Assistant Operating System.
- Once completed, you can access Home Assistant by opening a web browser and navigating to
http://homeassistant.local:8123. - If you encounter issues with the hostname, try accessing it via
http://homeassistant:8123or[your_VM_IP]:8123.
Étape 8 - Onboarding:
- With Home Assistant installed, follow the onboarding process to set up your user account and configure integrations.
- You can also install additional add-ons and customize your smart home setup.
Étape 9 - Important Notes:
- Running Home Assistant Core directly on Windows is not supported. Use the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to install Home Assistant Core.
- The provided VDI image contains the Home Assistant Operating System, which is a lightweight and optimized environment for running Home Assistant.
Remember to explore Home Assistant’s extensive documentation and community forums for further guidance and customization options. Enjoy building your smart home! 🏡
Published


 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português