Matériaux
Outils
Étape 1 - Setting up the weather station
Follow the instructions on page 1-4 on this tutorial.
Étape 2 - Monitoring the values recorded by the station via Blynk
Follow the instructions on page 4-8 on this tutorial.
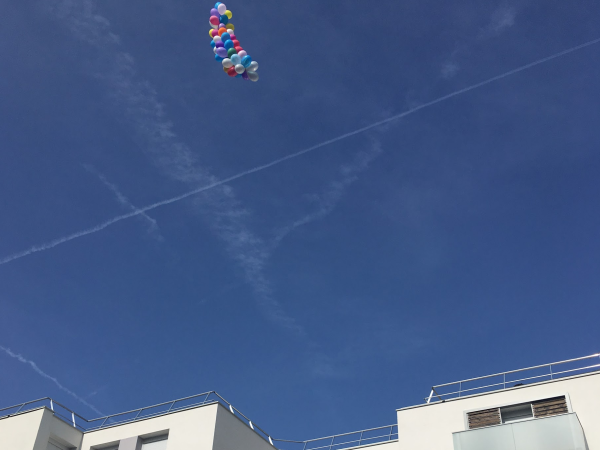
Étape 3 - Setting up the flying station
In order to send your weather station up in the air, first of all you ll need to engineer a system similar to that of a hot air balloon.
Create a case to accommodate the weather station. This can be made of cardboard or any other material, as long as the weight is not too significant. Beware that helium balloons can only lift very light masses.
Once you've secured the weather station to the case, attach the former to the helium balloons. You may need to use multiple balloons in order to be able to lift the weather station off the ground.
Don’t forget to tie some nylon wire to the flying system so that you ll be able to take it back to the ground at any time.
Étape 4 - Plotting the values recorded by the station on UMap
You will be sharing the data recorded by your water probe on UMap, which allows users to create their own maps embedding the data of their choice.
First, head to https://umap.openstreetmap.fr/fr/
You ll need to create an account to be able to edit your own maps.
Once you have successfully logged in, hit the “Create a map” button.
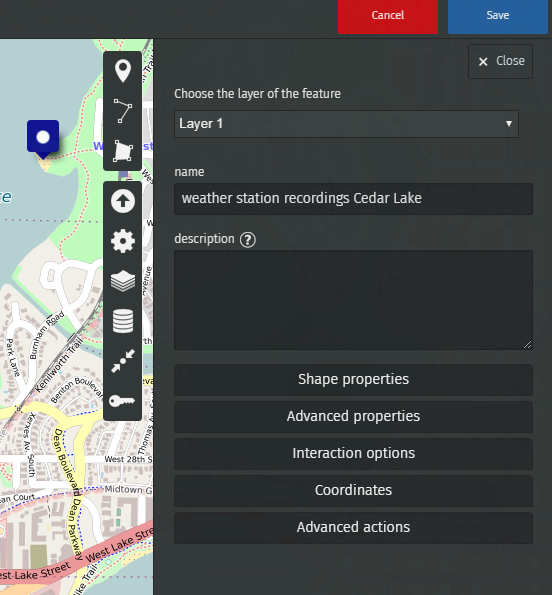
You can now draw markers and enter any description you wish to publish.
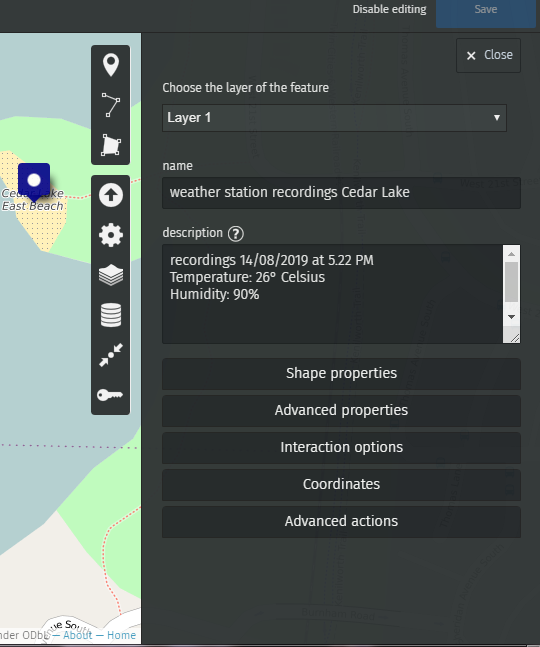
Let’s add a marker featuring the recordings of the weather station above Cedar Lake, in Minneapolis.
Today the temperature in the air above Cedar Lake is 26° Celsius and the humidity is 90%. Indeed, it is raining!
Once you’re done, hit the Save button.
To share this map with anyone, you just need to provide them with the appropriate link.
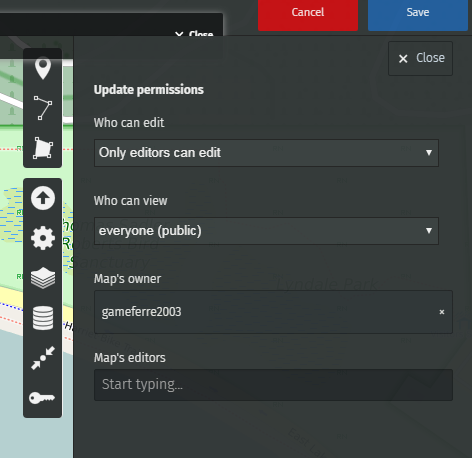
Go to Update permissions and editors.
You can choose who can view and who can edit this map.
To enable editors to edit the map, copy the link of your map (the web address of your map) and share it with whoever you want.
Notes et références
List of parts
1x ESP32 weather station
1x nylon wire bobbin
Draft


 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português