(Page créée avec « 3 par filtre. La largeur doit être 10-15% plus grande que la largeur intérieure du boîtier du filtre, dans ce cas 115 mm. Découper au laser (faible puissance) ou en ci... ») |
(Page créée avec « '''Couvercles pour régulateur de débit''' Les régulateurs de débit ressemblent aux filtres mais avec une seule entrée et plusieurs sorties pour le régulateur de déb... ») |
||
| Ligne 50 : | Ligne 50 : | ||
|Step_Content=3 par filtre. La largeur doit être 10-15% plus grande que la largeur intérieure du boîtier du filtre, dans ce cas 115 mm. Découper au laser (faible puissance) ou en ciseaux la membrane de tissu. | |Step_Content=3 par filtre. La largeur doit être 10-15% plus grande que la largeur intérieure du boîtier du filtre, dans ce cas 115 mm. Découper au laser (faible puissance) ou en ciseaux la membrane de tissu. | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Couvercles pour régulateur de débit''' |
| − | + | Les régulateurs de débit ressemblent aux filtres mais avec une seule entrée et plusieurs sorties pour le régulateur de débit du bas et inversement pour celui du haut. | |
}} | }} | ||
{{ {{tntn|Tuto Step}} | {{ {{tntn|Tuto Step}} | ||
Version du 18 novembre 2018 à 23:07
Sommaire
- 1 Étape 1 - Fabriquer les composants
- 2 Étape 2 - Couper les couvercles pour le filtre
- 3 Étape 3 - Découper les disques de compression
- 4 Étape 4 - Découper les tissus
- 5 Étape 5 - Caps for UV lamp
- 6 Étape 6 - Cut the Filter Housing Pipe
- 7 Étape 7 - Make waterproof gaskets
- 8 Étape 8 - Assemble the flow regulators (1)
- 9 Étape 9 -
- 10 Étape 10 - Then do the lid on the other side.
- 11 Étape 11 -
- 12 Étape 12 -
- 13 Étape 13 -
- 14 Étape 14 - Place the lid on a flat surface and add the pipe
- 15 Étape 15 -
- 16 Étape 16 -
- 17 Étape 17 -
- 18 Étape 18 -
- 19 Étape 19 -
- 20 Étape 20 -
- 21 Étape 21 -
- 22 Étape 22 -
- 23 Étape 23 -
- 24 Étape 24 -
- 25 Étape 25 - Tada!
- 26 Commentaires
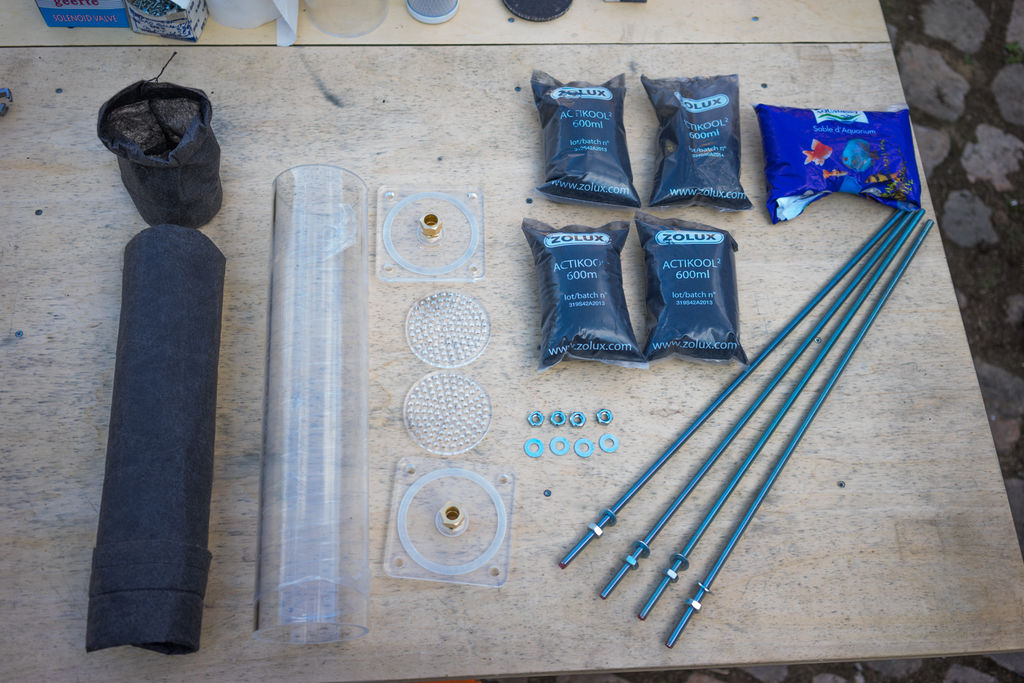
Étape 1 - Fabriquer les composants
Couper au laser ou à la machine CNC les fichiers de this pdf.
Comme les découpeurs laser gèrent la découpe un peu différemment, il peut y avoir des problèmes avec le fichier. Généralement, les repères rouge (0.001mm) sont pour la découpe et le noir pour la gravure.
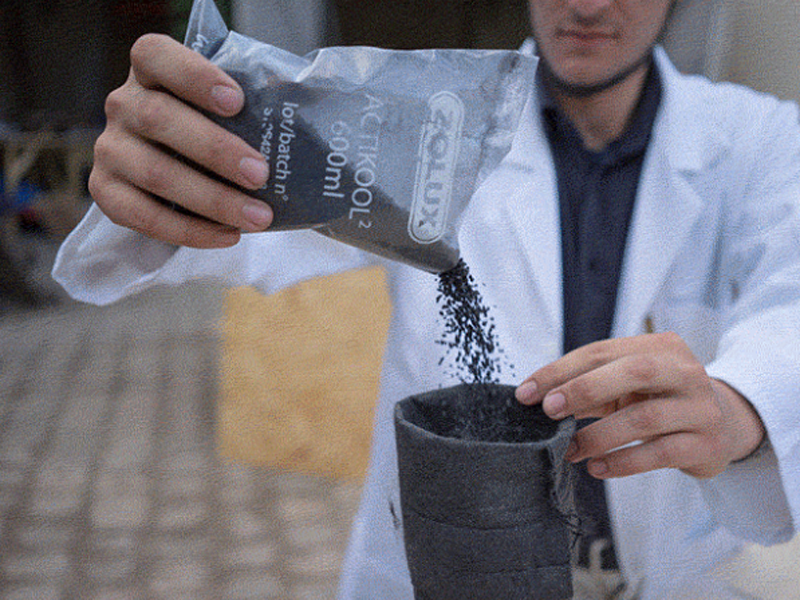
Les couvercles et les plaques de support peuvent également être une seule et même pièce si vous utilisez un matériau épais. Quatre filtres de 10 cm de diamètre x 50 cm sont nécessaires pour obtenir un débit convenable de 10 l/min. Avec 6.6l/min, deux filtres suffisent et un seul filtre pour 3.3l/min. La surface spécifique est plus importante que la longueur du filtre car elle détermine le débit à travers le filtre et donc les temps de réaction. J'utilise des feuilles acryliques de 10 mm d'épaisseur pour le couvercle et les disques de compression, mais j'ai utilisé des feuilles acryliques de 4 à 5 mm dans les prototypes précédents et je les ai collées avec de bons résultats.
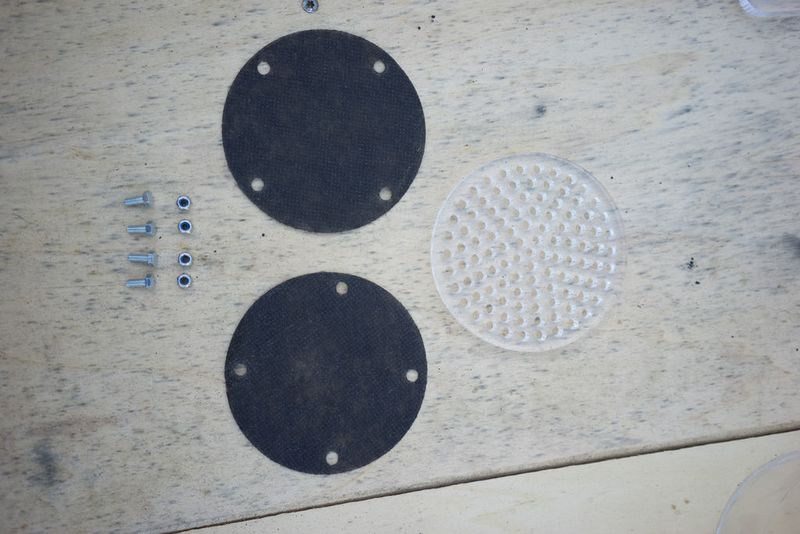
Étape 2 - Couper les couvercles pour le filtre
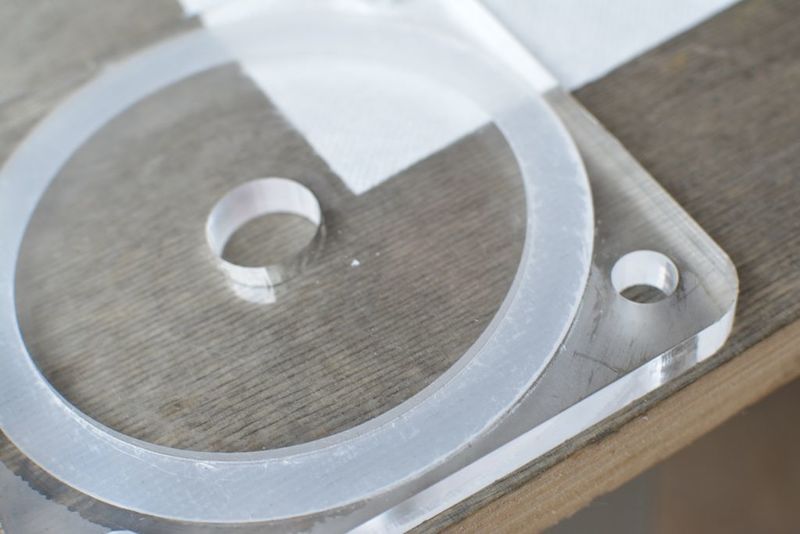
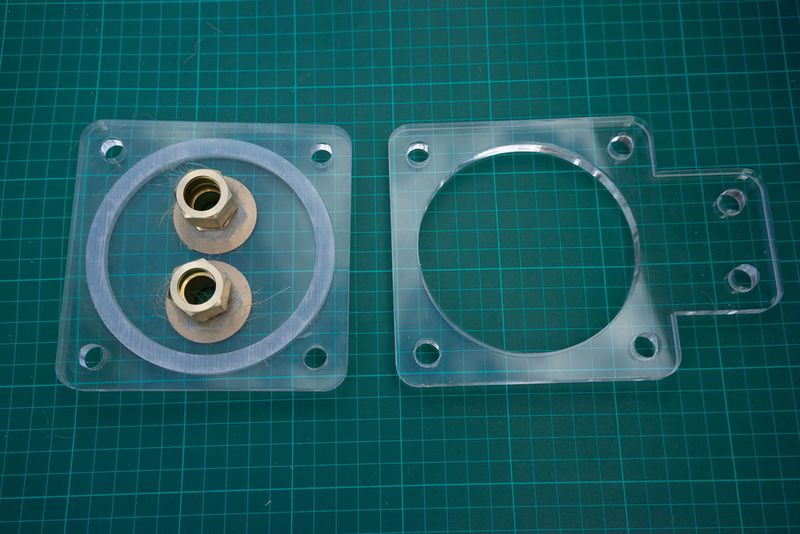
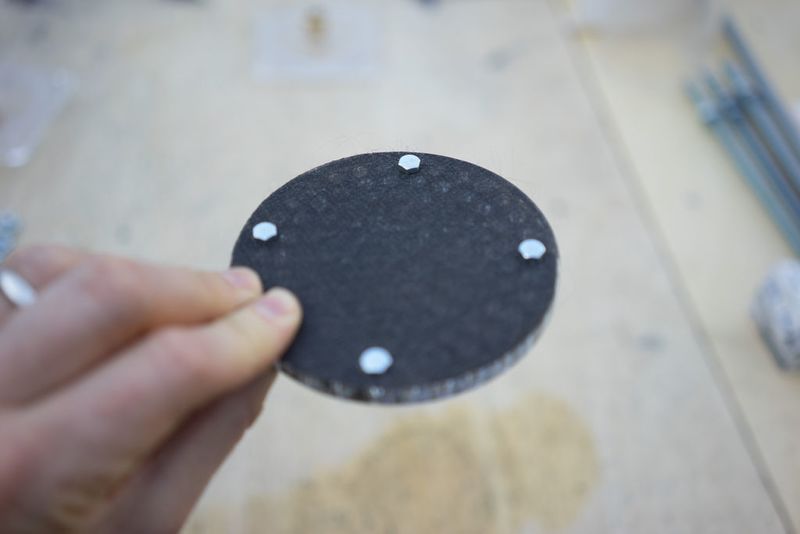
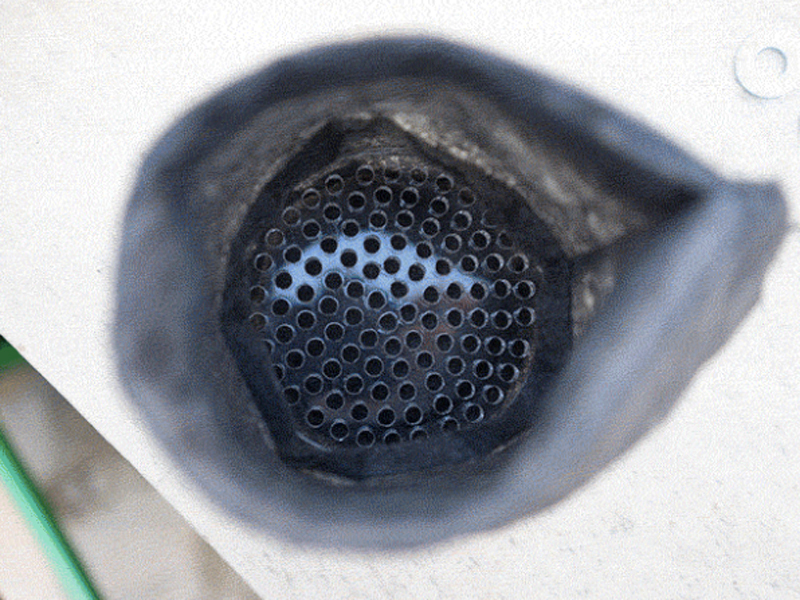
Il y a 2 couvercles par filtre, le couvercle supérieur et le couvercle inférieur - sans blague ?
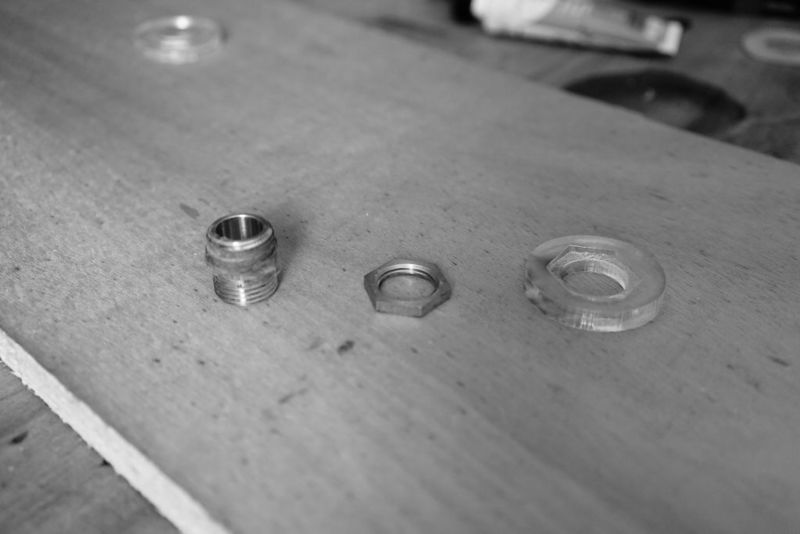
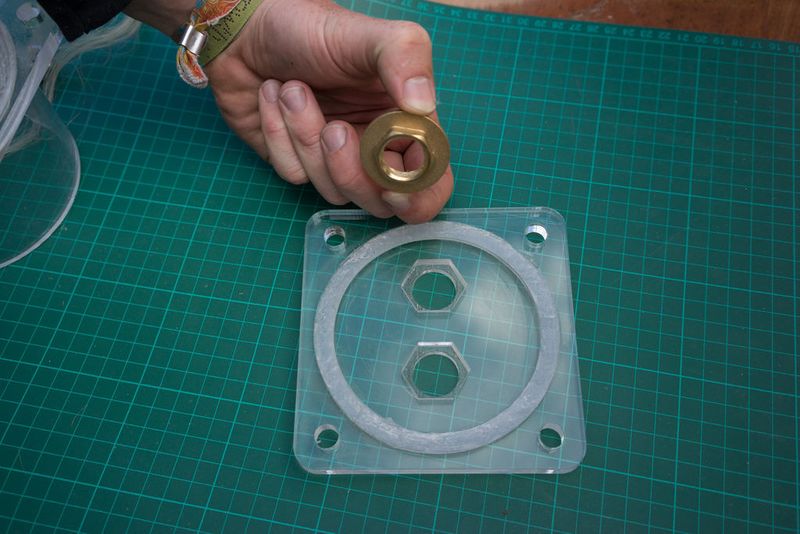
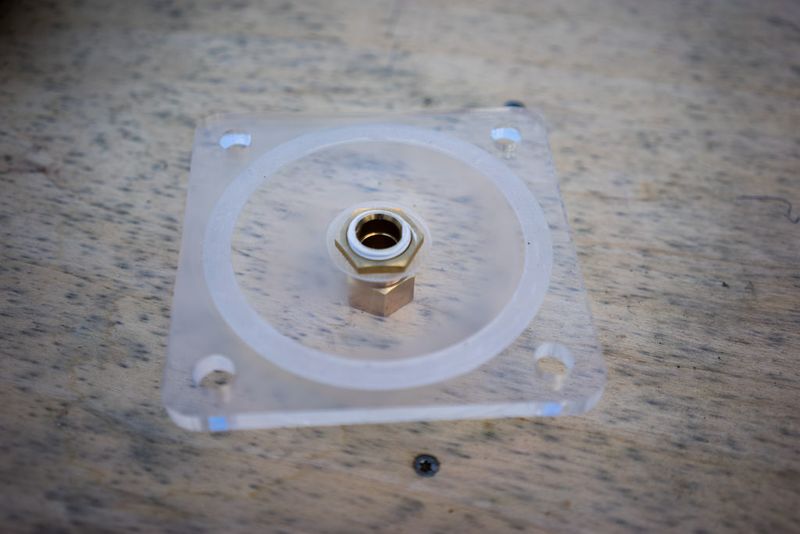
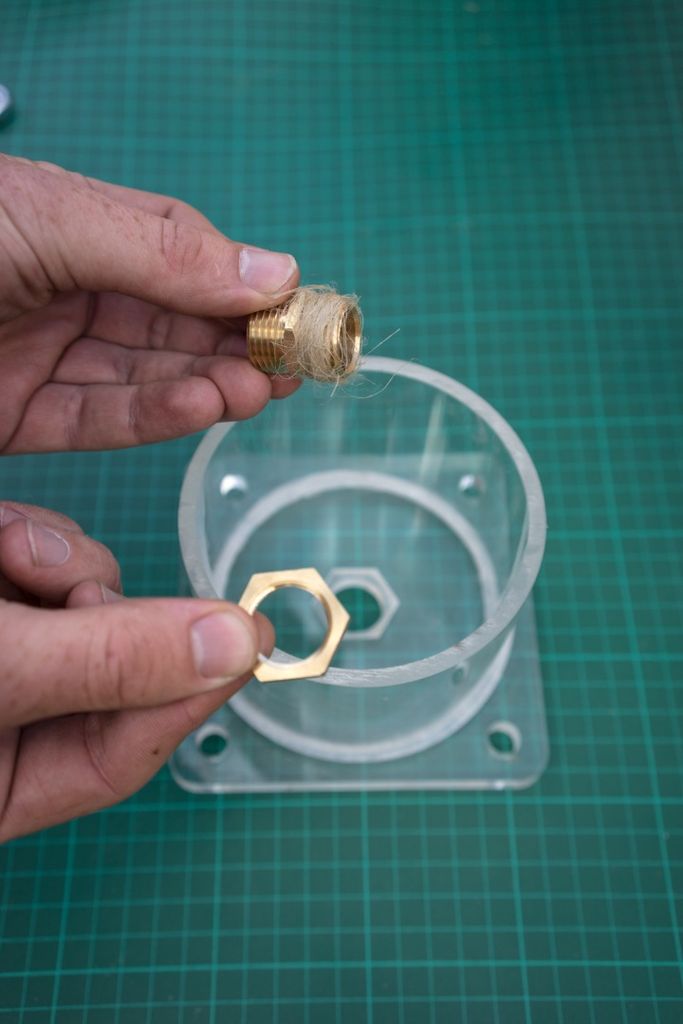
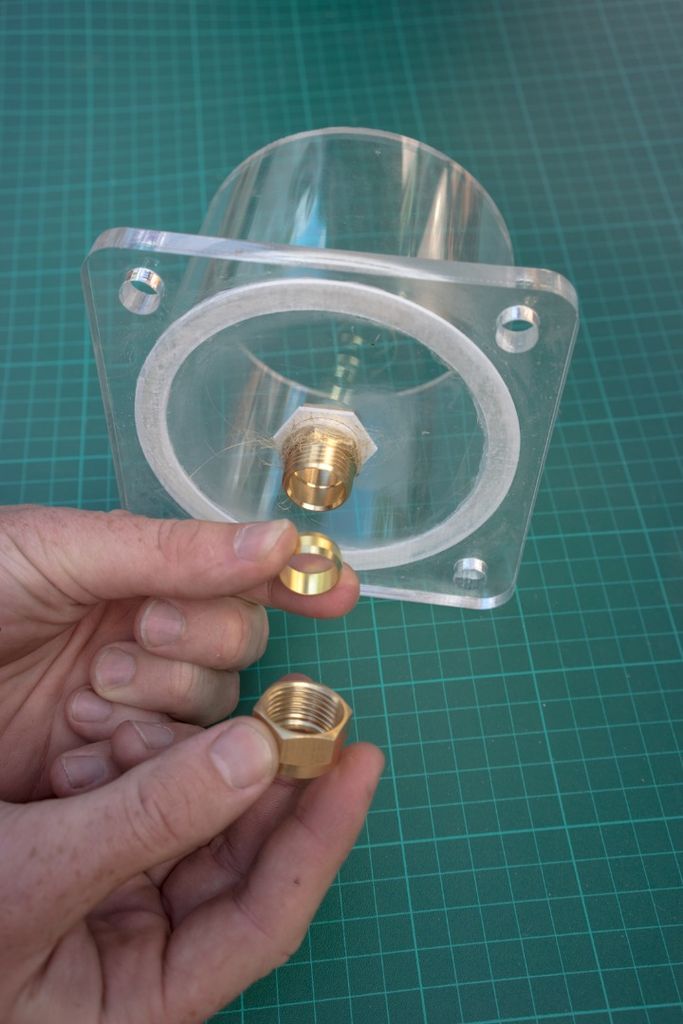
Un écrou hexagonal est utilisé pour fixer le raccord du tuyau (opposé au filtre) au couvercle du filtre. Les dimensions des écrous hexagonaux et/ou des raccords de flexibles peuvent varier d'une région à l'autre. Il est donc préférable de les obtenir en premier, de vérifier les mesures et de modifier le fichier si nécessaire. Sur l’image du couvercle, seul un cercle a été gravé/fraisé dans le couvercle en acrylique afin de l’adapter à l’écrou hexagonal, mais la conception a été modifiée ultérieurement pour prendre la forme de l’écrou hexagonal lui-même, le fixant ainsi au couvercle afin qu’il ne puisse plus tourner (et éviter qu'il ne se ferme) lorsque vous ajoutez le raccord de tuyau sur le côté extérieur du couvercle.
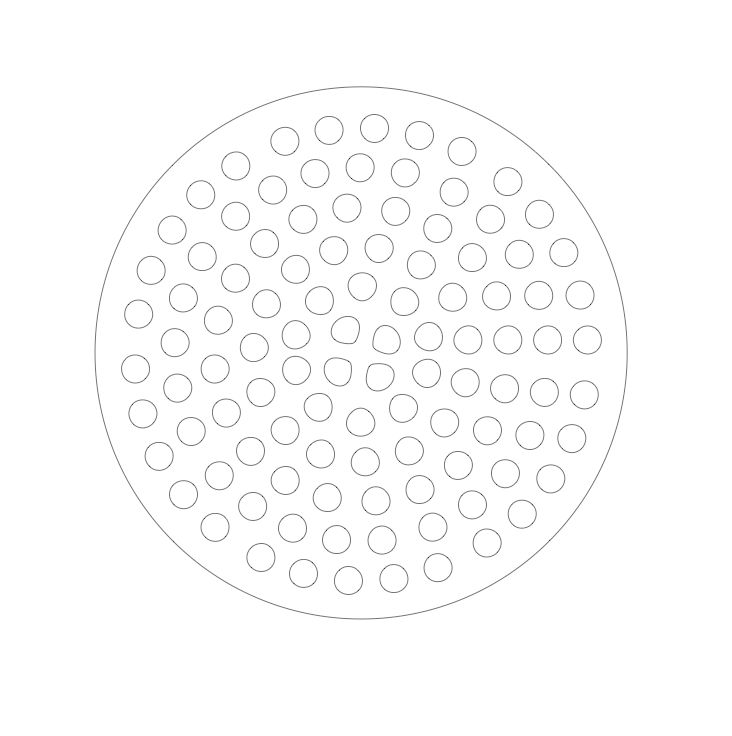
Étape 3 - Découper les disques de compression
Il y a 3 disques de compression par filtre. Deux aux deux extrémités pour compresser le sable et le charbon actif et un entre le sable et le charbon actif! Le disque de compression dans le fichier est imbriqué dans le vide de la plaque de support pour économiser du matériel!
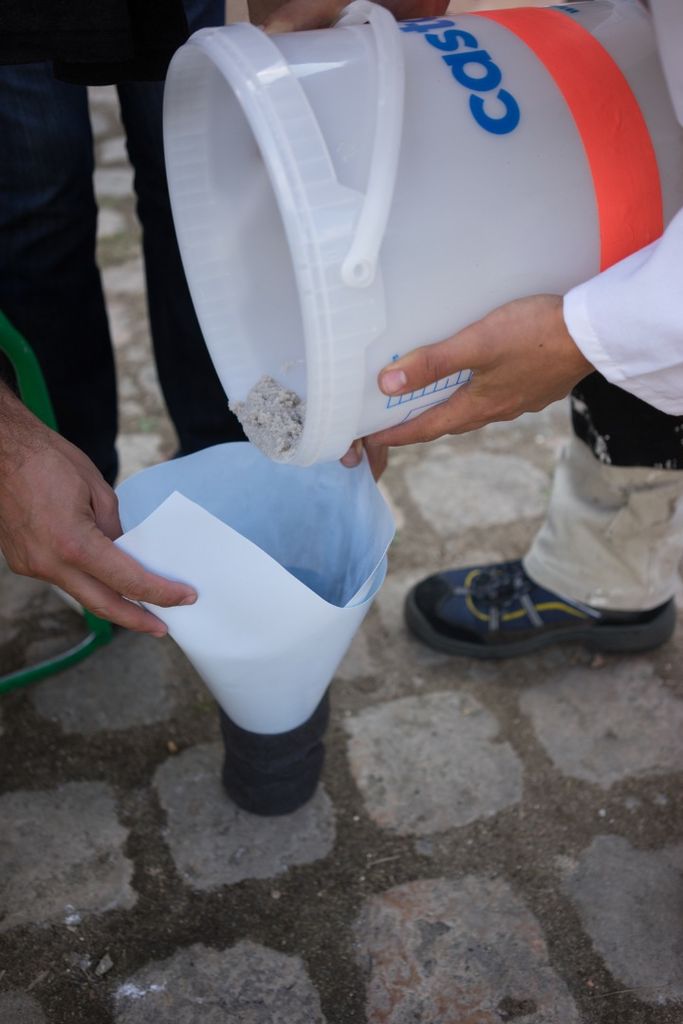
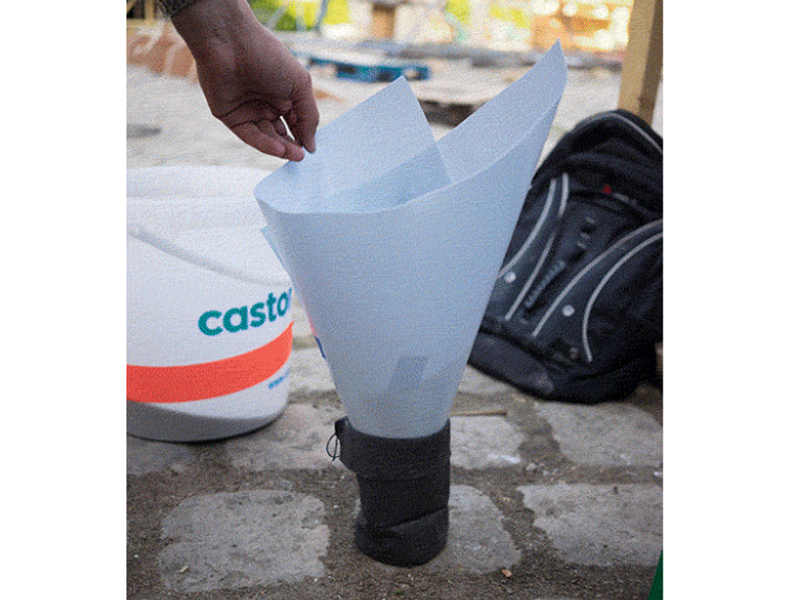
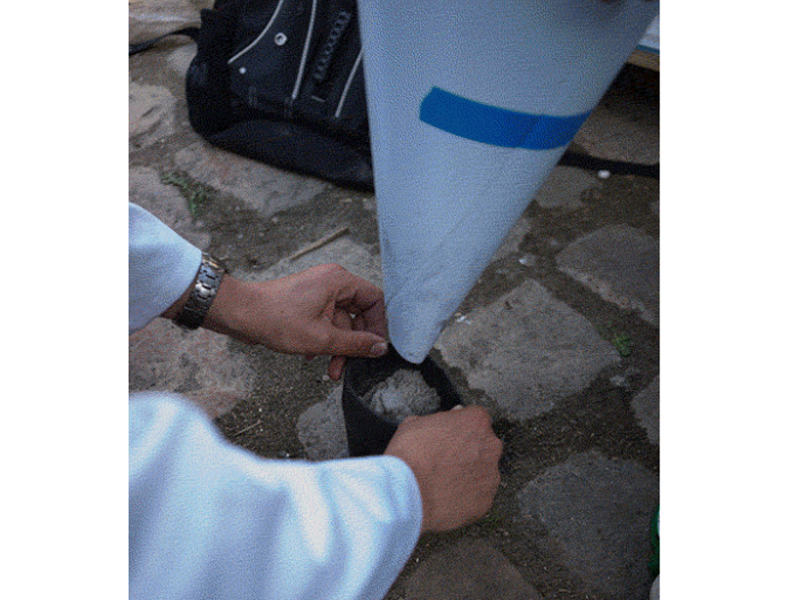
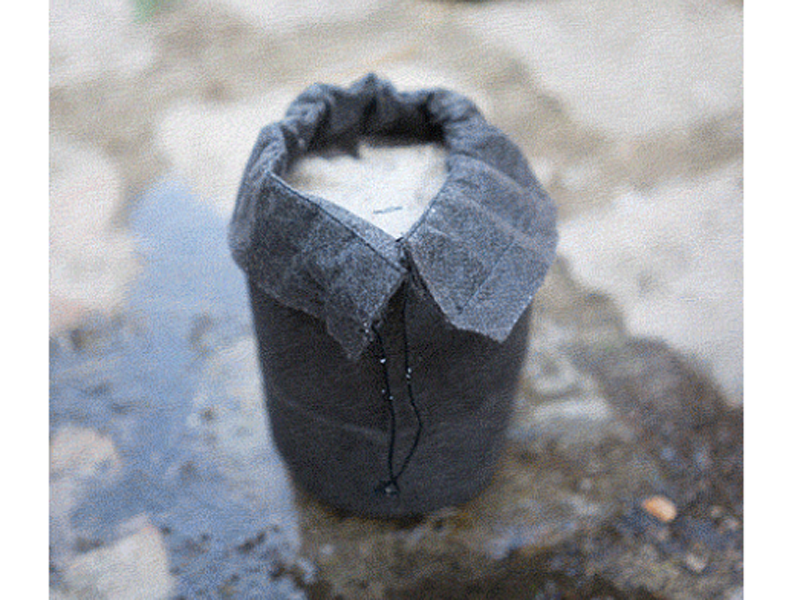
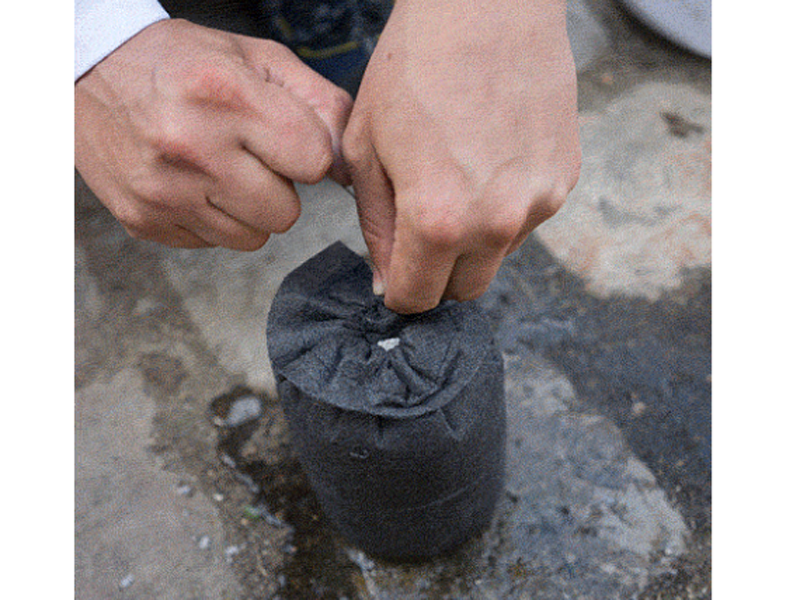
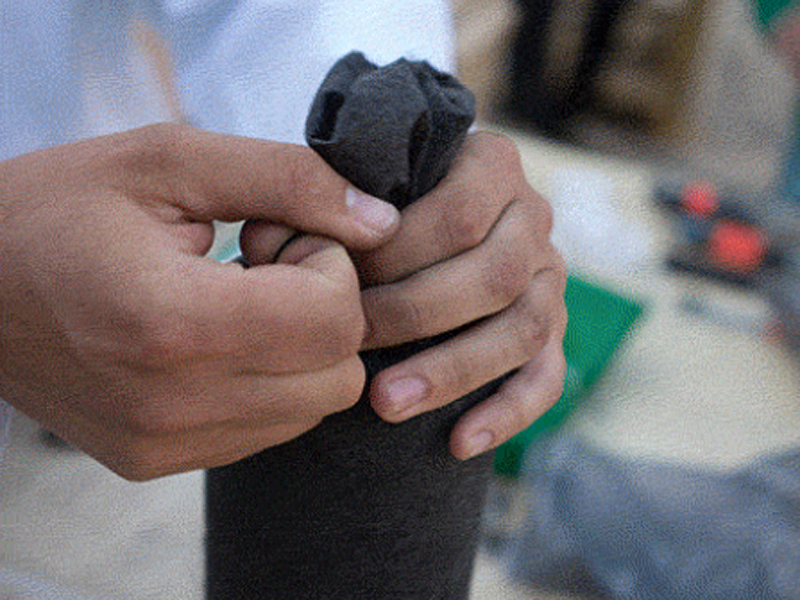
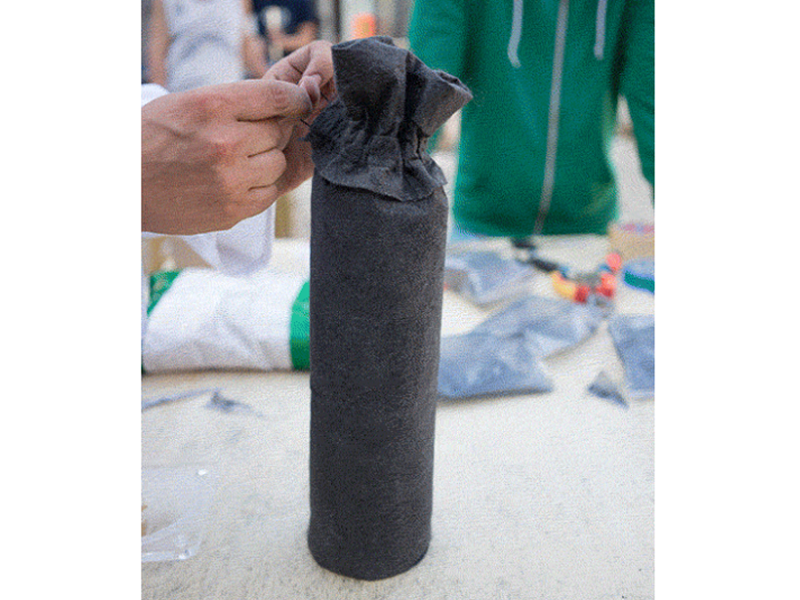
Étape 4 - Découper les tissus
3 par filtre. La largeur doit être 10-15% plus grande que la largeur intérieure du boîtier du filtre, dans ce cas 115 mm. Découper au laser (faible puissance) ou en ciseaux la membrane de tissu.
Couvercles pour régulateur de débit Les régulateurs de débit ressemblent aux filtres mais avec une seule entrée et plusieurs sorties pour le régulateur de débit du bas et inversement pour celui du haut.
Étape 5 - Caps for UV lamp
The cap is on the far right. A dip is etched into it to fit the hexnut/lock nut in the same way as in the filter lid. The Male-male brass union fastened to the UV cap is what allows the water tight connection between the UV lamp and piping. Special care should be taken with this UV cap because Acrylic will still let UV light through, while not included in the following picture sets the outer side of the cap should be coated in white paint (with titanium dioxide) or otherwise taped up so that you don't get exposed to the light directly.
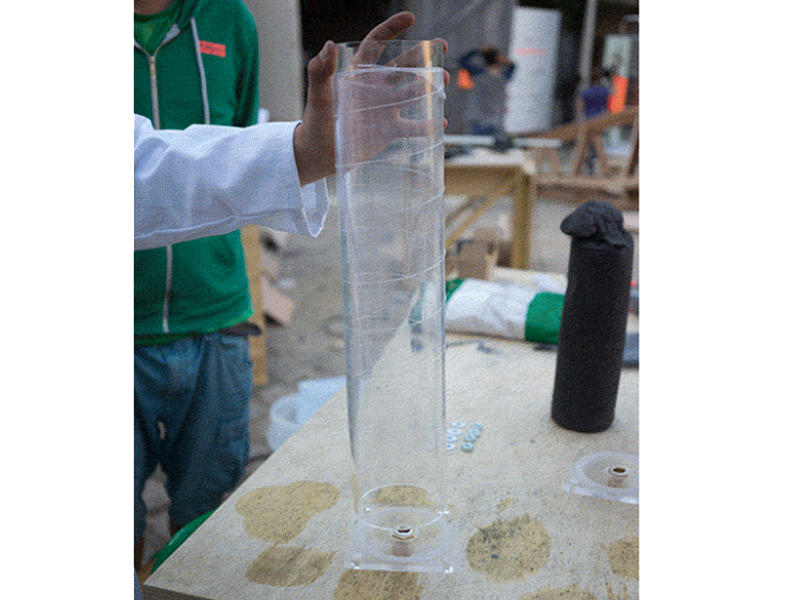
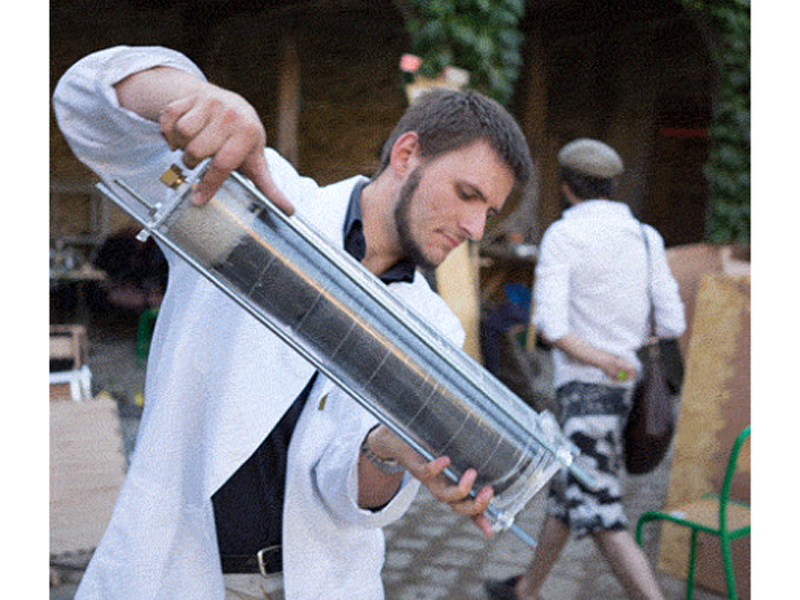
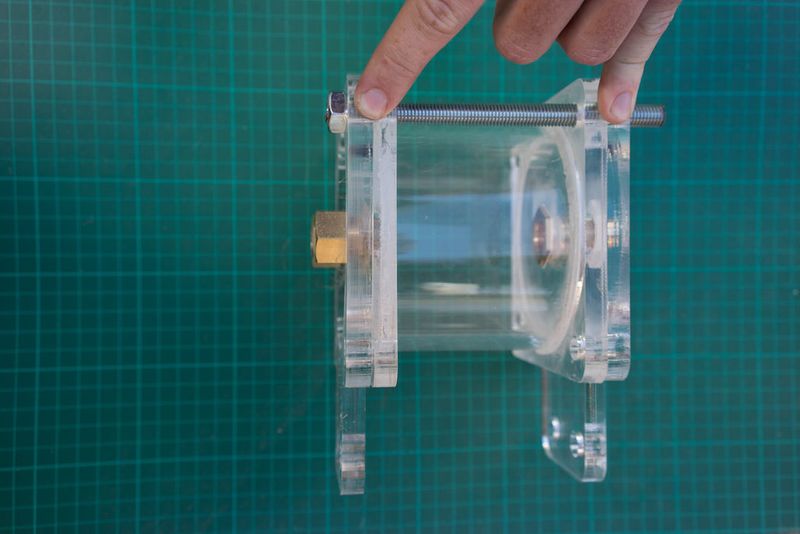
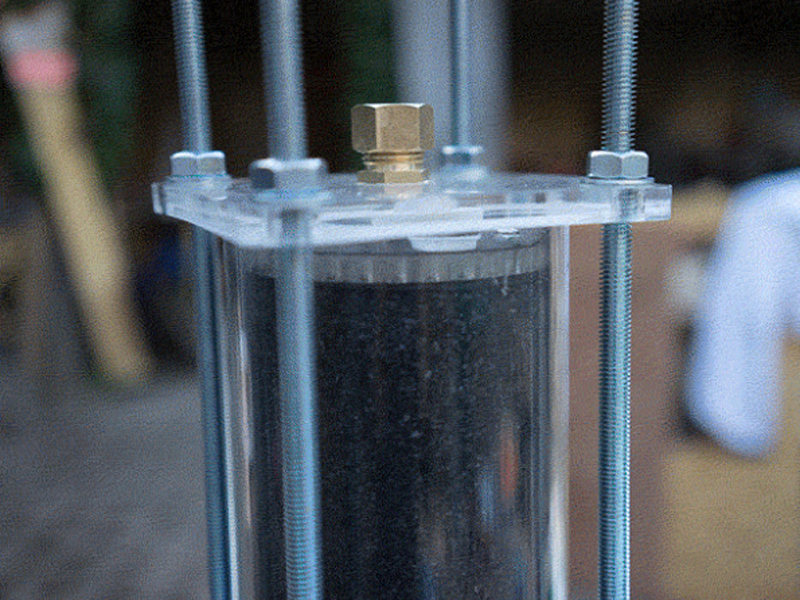
Étape 6 - Cut the Filter Housing Pipe
Cut the transparent acryclic pipe with a band saw if available or with a hand saw.
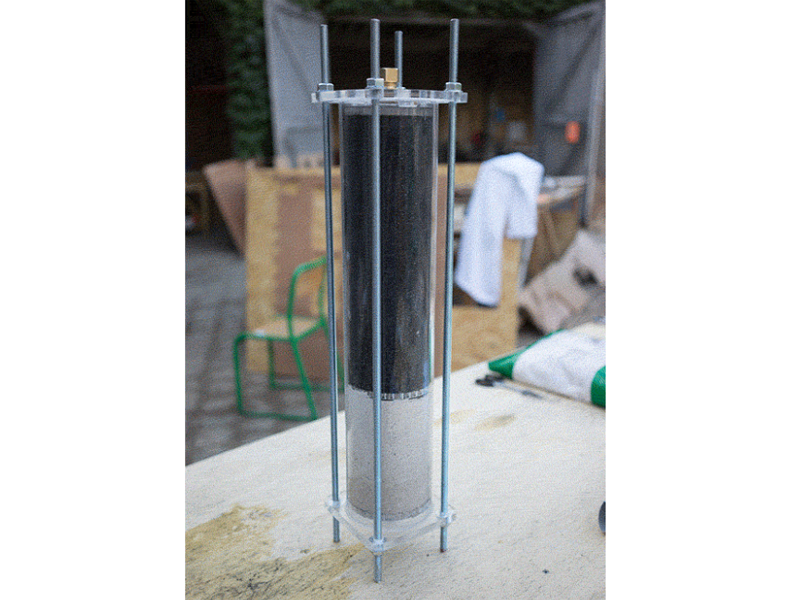
The filter housings should be 55 cm long and the flow regulator pipe should be around 10 cm long but shorter bits may work just as well and therefore require less water. The flow regulators can be left out of the build completely but there's something great about being able to see dirty water in the lower one get cleaned up by the filters and to get visual feedback in the top one which should be around eye height.
To get a straight cut the following videos are pretty helpful. The gist is to use lined up tape to get a perfect straight line around the pipe and cut around them. With a band saw you can use the leveller (aligning tool) to keep the cut straight. Because acrylic works a lot like wood you can level or adjust the cutting with sandpaper.
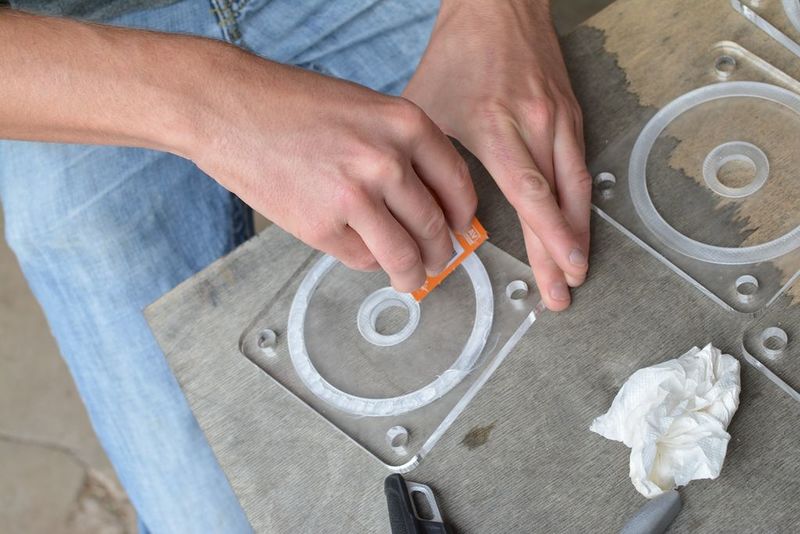
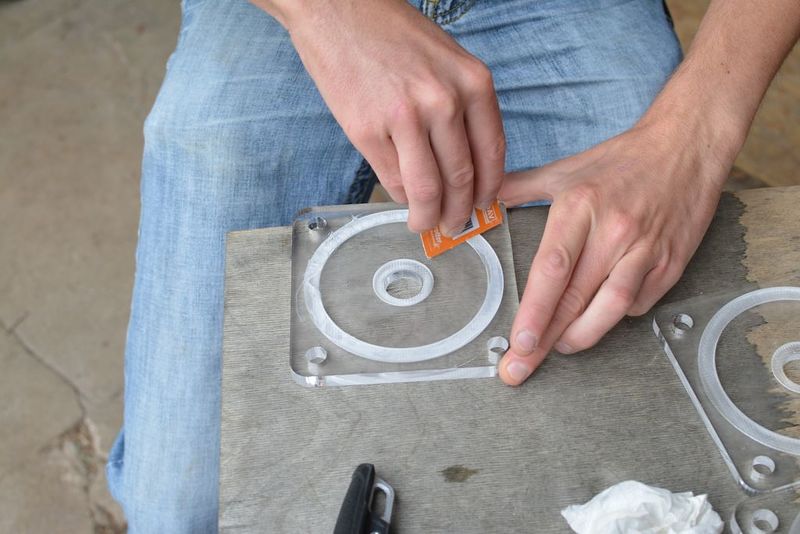
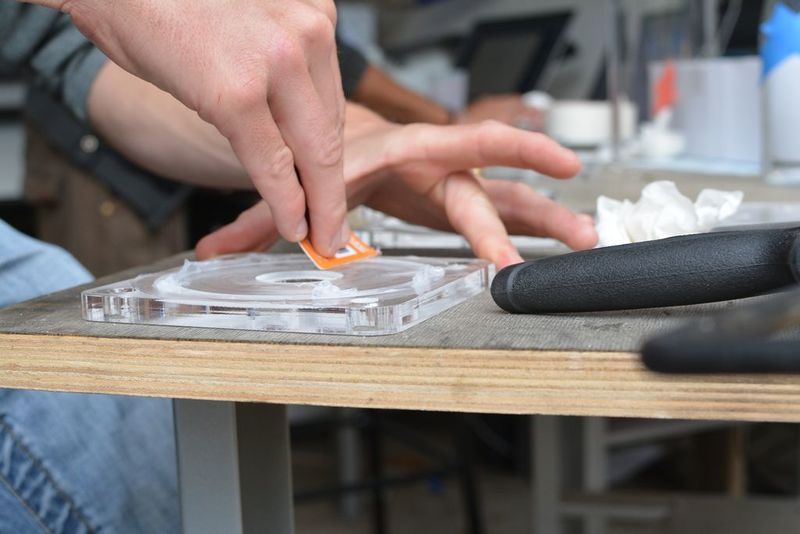
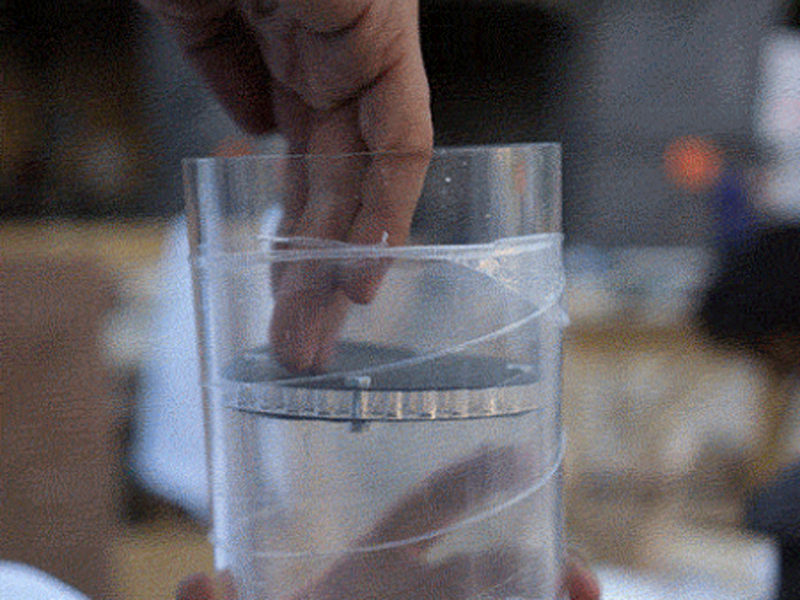
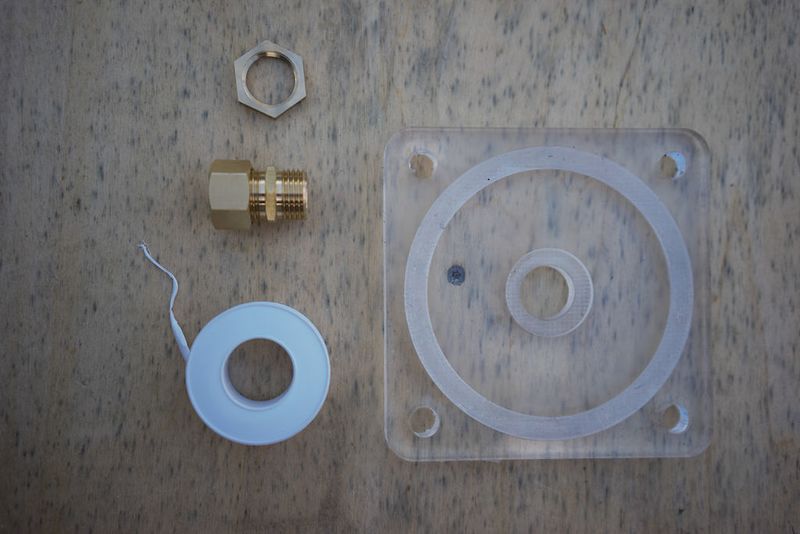
Étape 7 - Make waterproof gaskets
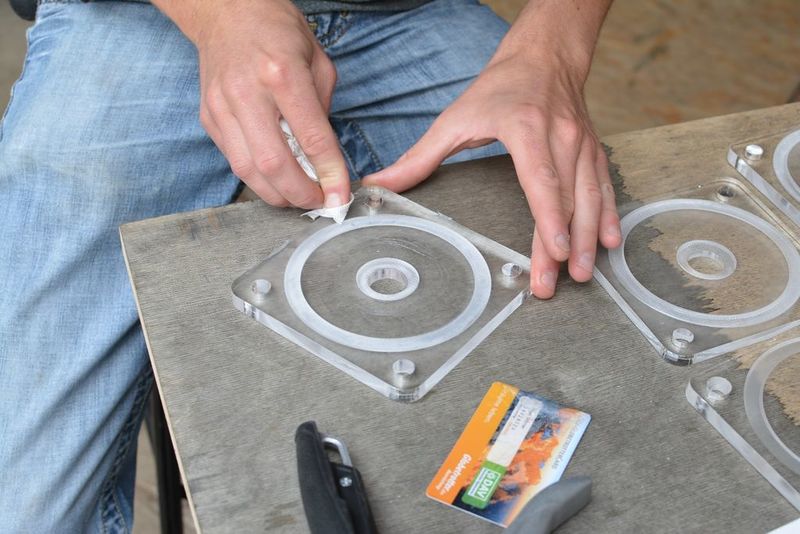
This step can be skipped by milling a gasket out of silicone sheets with the same depth as the 'trough' in the lid. I don’t have much advice on material selection (rubber or silicone) but there are specialist stores that could provide solid advice. I use silicone sheets. The material is best laser cut to the dimensions of the trough mentioned above. The .ai file can be found above (Gasket.pdf) Using a ‘silicone gun’ fill the circular trough with silicone up to the surface level. Use a plastic card such as a membership card you don’t mind getting a bit dirty, and with force, slide the flat surface across and over the silicone. It’s ok if it goes over or gets dirty as it can be cleaned later. Make sure that there are no bubbles or distortions in the silicone. The surface of the lid can now be cleaned toilet paper but avoid areas near the trough until it has hardened ~24 hours later. The silicone is easier to rub off once it’s dry.
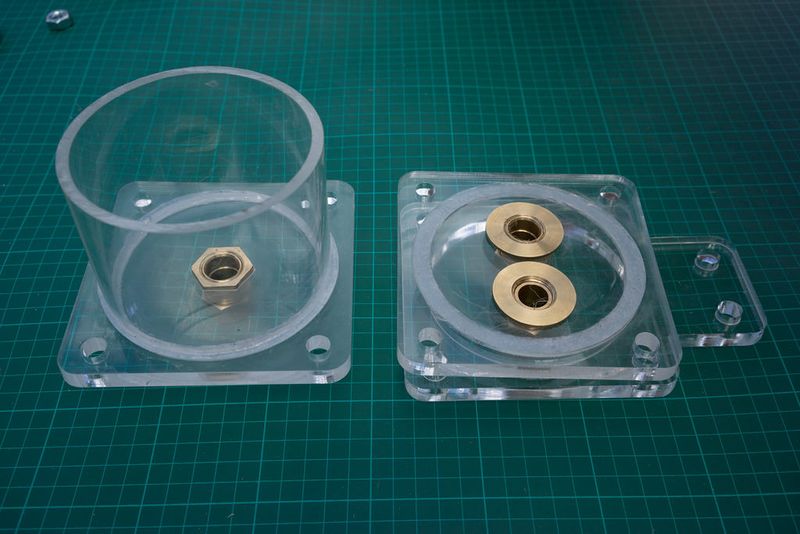
Use a gasket or silicone in a similar fashion as mentioned above to connect the lower lids to the tubes. Fill the trough as mentioned in the steps above but instead of letting the material dry, press the cylinder into the lid, clamp together and then leave to dry (24 hours ideally). The silicone can be smoothed out with a gloved finger. This also reduces the surface area for bacteria or dirt to attach too. The water pressure is highest at the bottom of the filter, and so fusing the tube together with the lower lid is a good idea since it makes the seal extra strong.
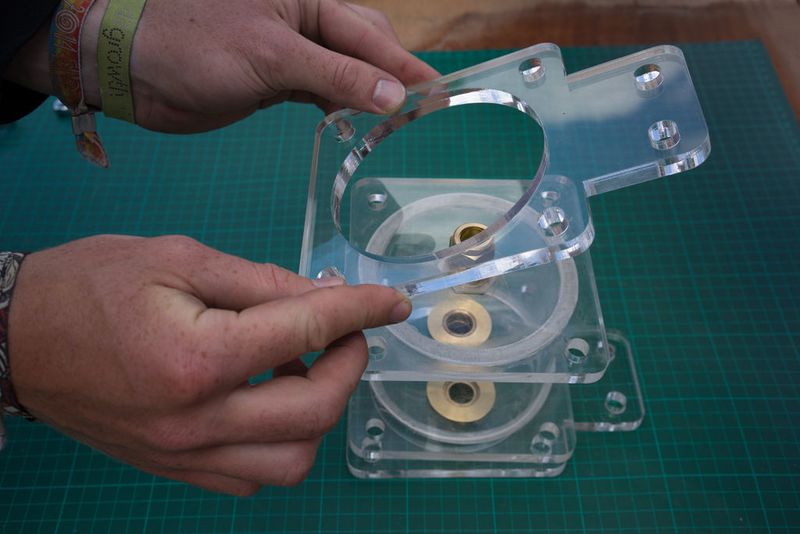
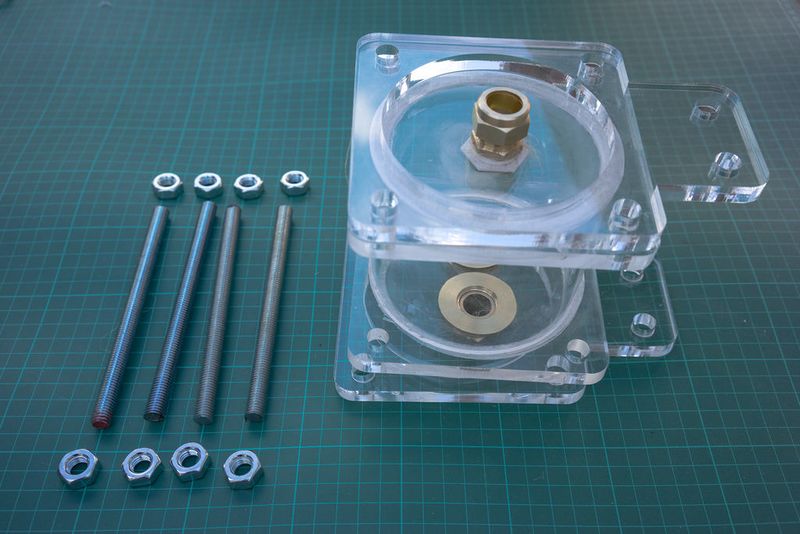
So the top lids for the filters and flow regulators are the removable ones that are allowed to dry, but the lower lids can be sealed together. If you use a milled gasket the filters will hold up on their own without the need for any silicone, but assembly is easier when one side is attached. It's also possible to use acryclic glue and chemically bond the materials together, but usually costs a lot more than silicone. It should last longer than the silicone on the other hand.
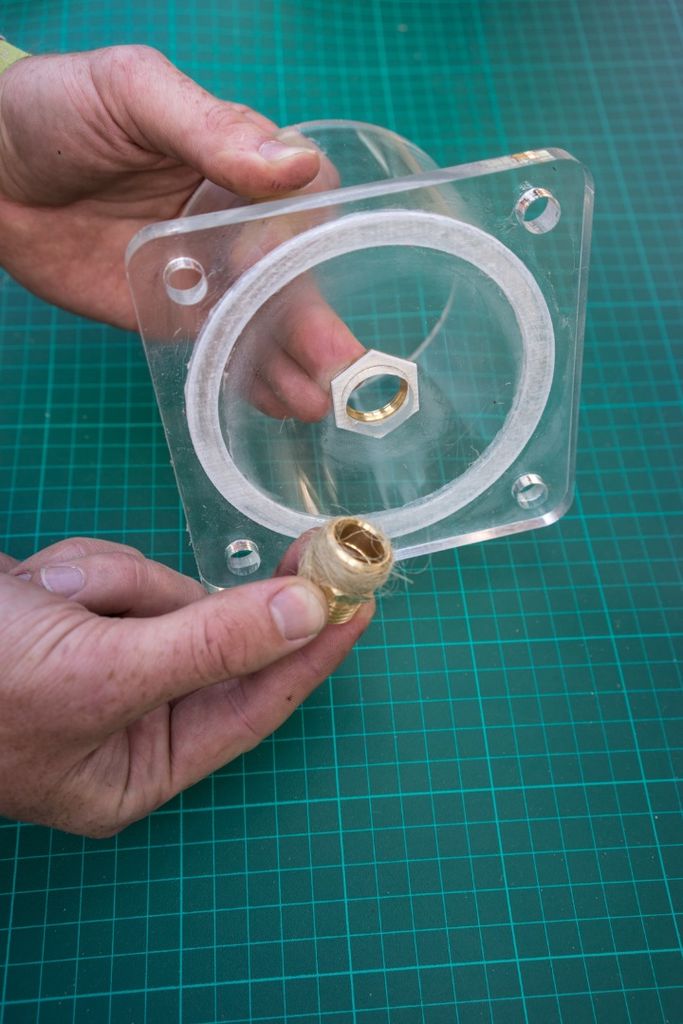
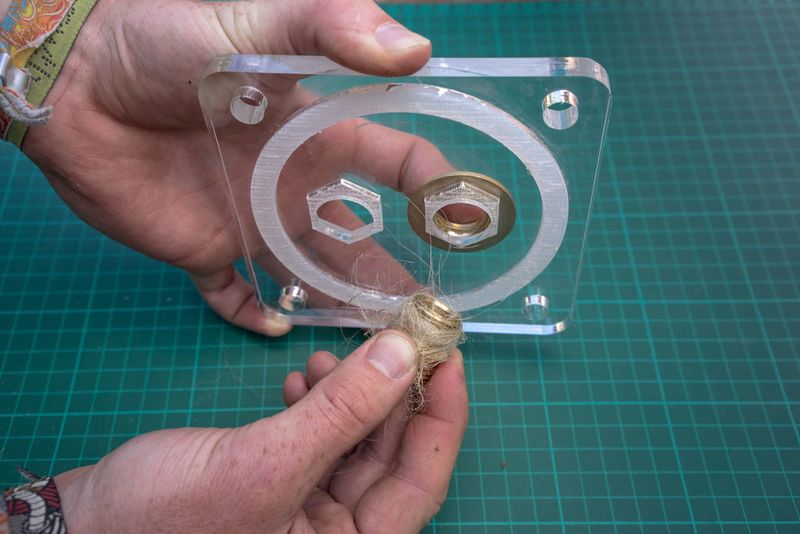
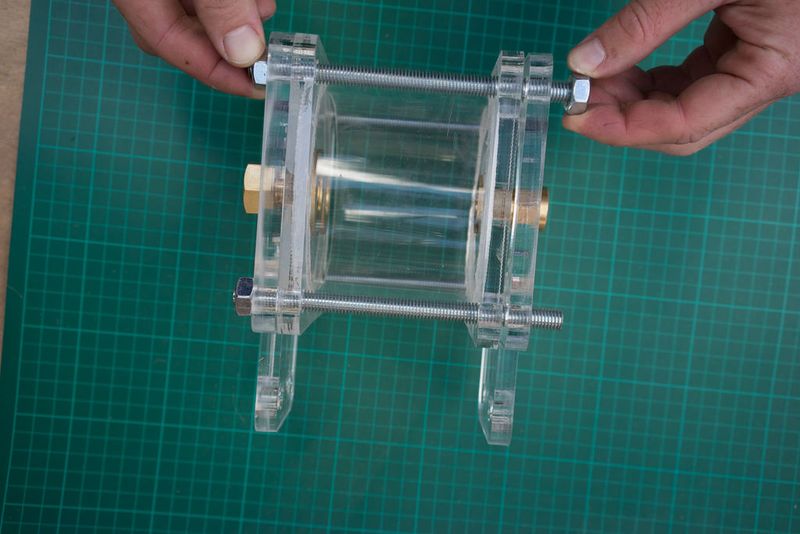
Étape 8 - Assemble the flow regulators (1)
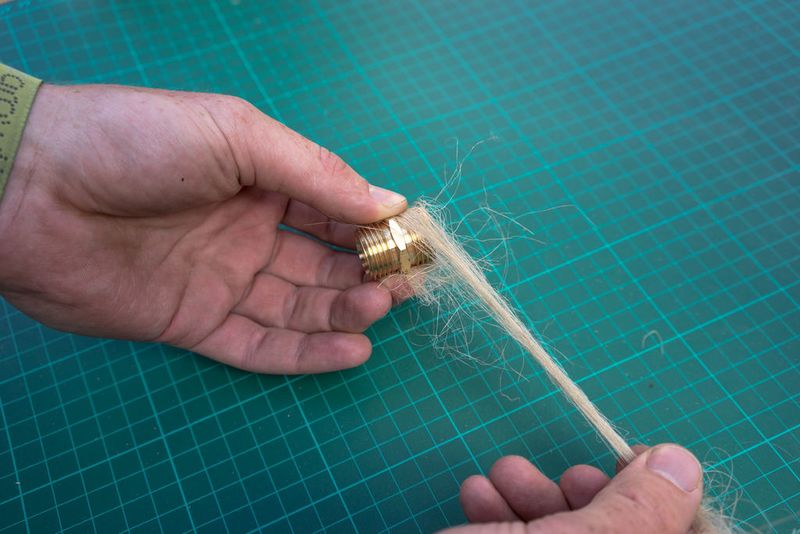
This part may take some practice figuring out just how much fibre to use. You can also replace the fibre with teflon tape (pipe tape) and as a rule of thumb I do about 8 layers (times around) but it depends on the size of the hole.
Étape 9 -
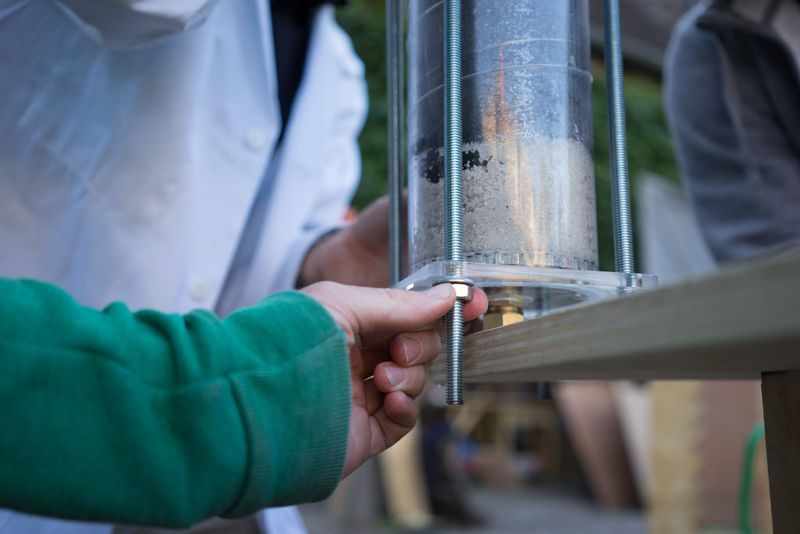
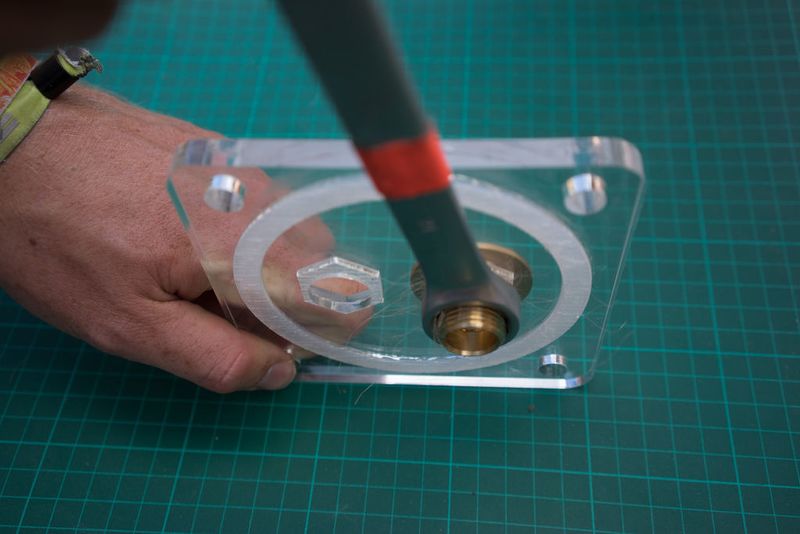
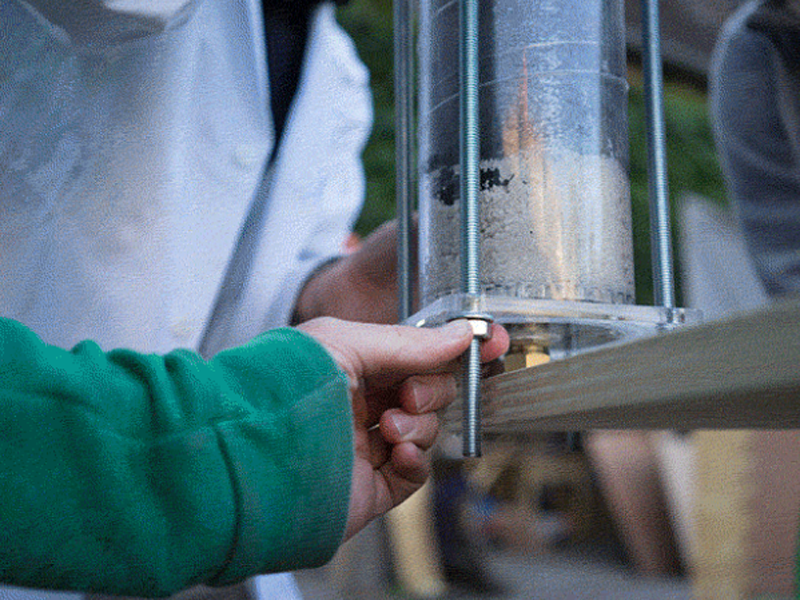
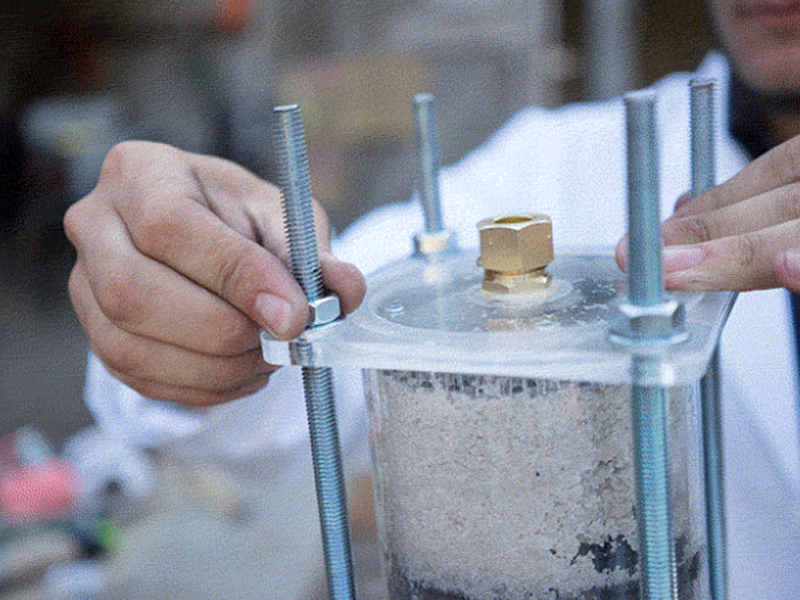
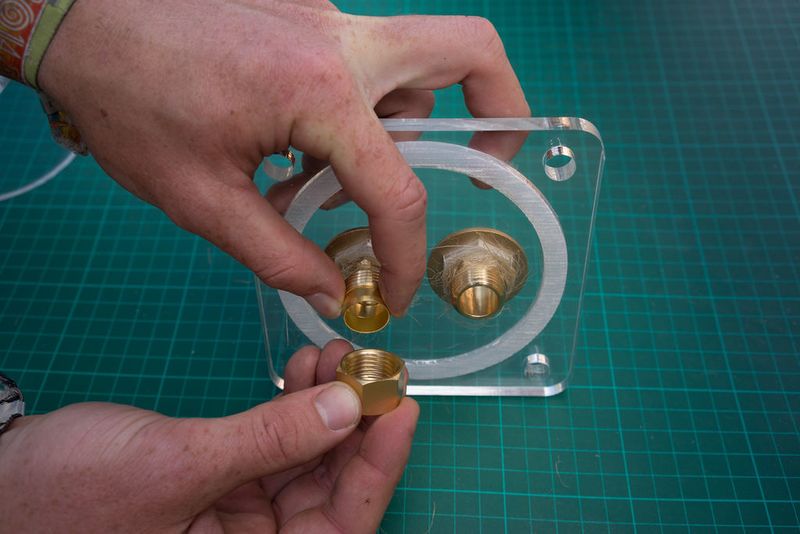
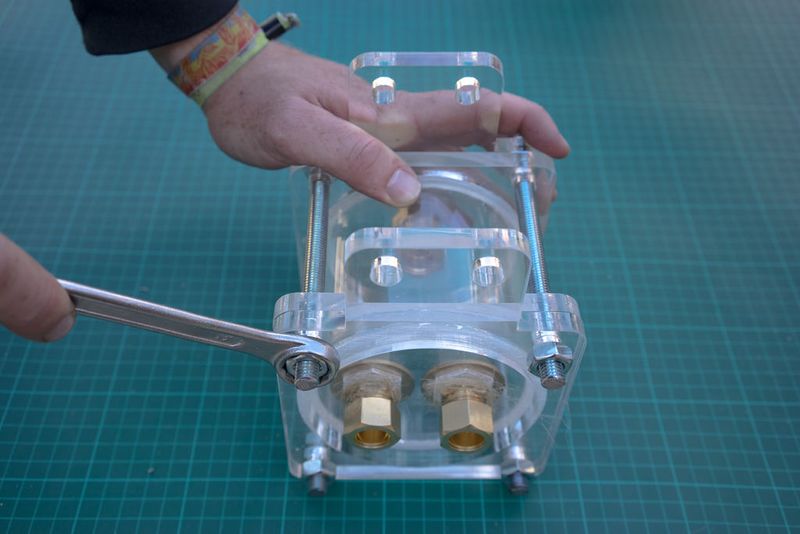
hold the lock nut in place while using a spanner to tighten the union to the lock nut. a hose nipple can also be used instead of the copper union.
Étape 13 -
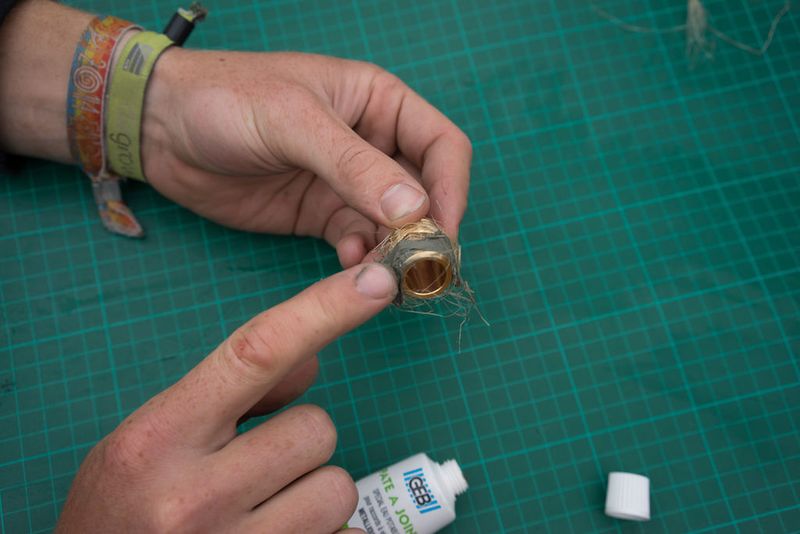
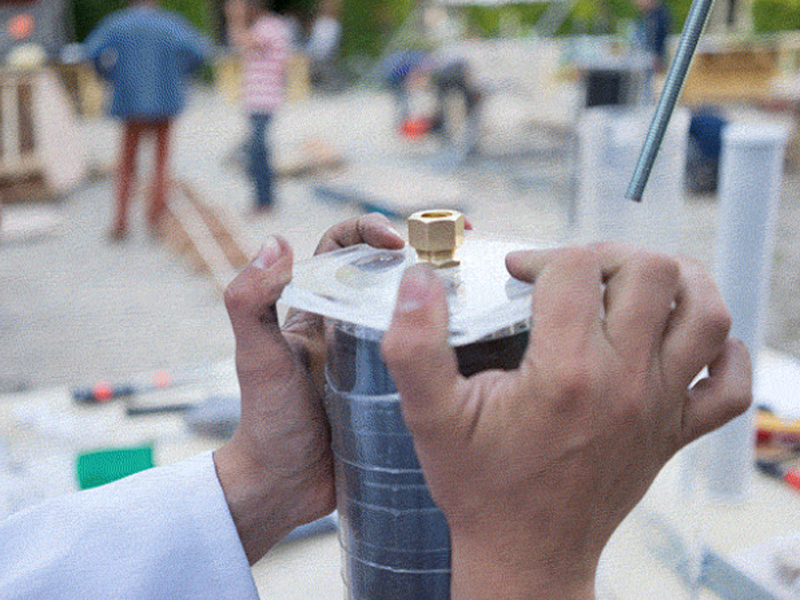
Slot the hexnut into the groove in the lid and screw in the brass male-male union (or male thread hose connector) on the flat outer side of the lid.
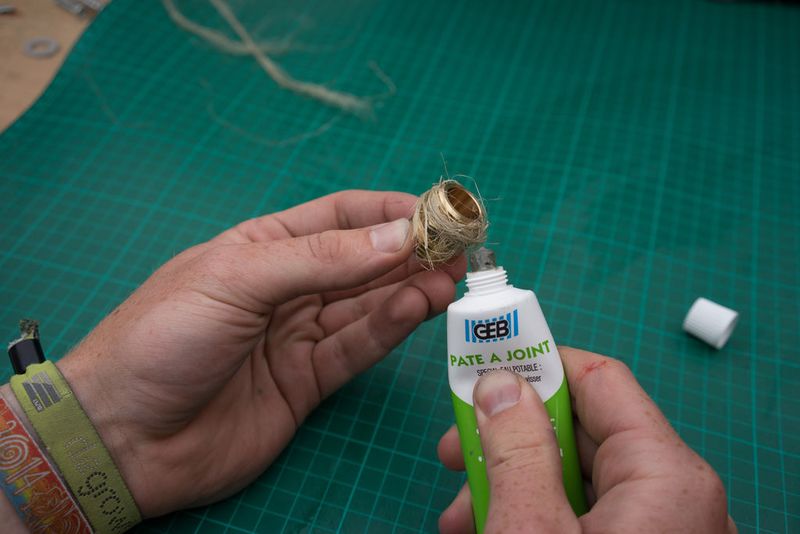
Use hemp fibre and mineral oil or a lot of teflon tape around the union and hex or + use silicone to seal the thing for good.
Do this for both lids.
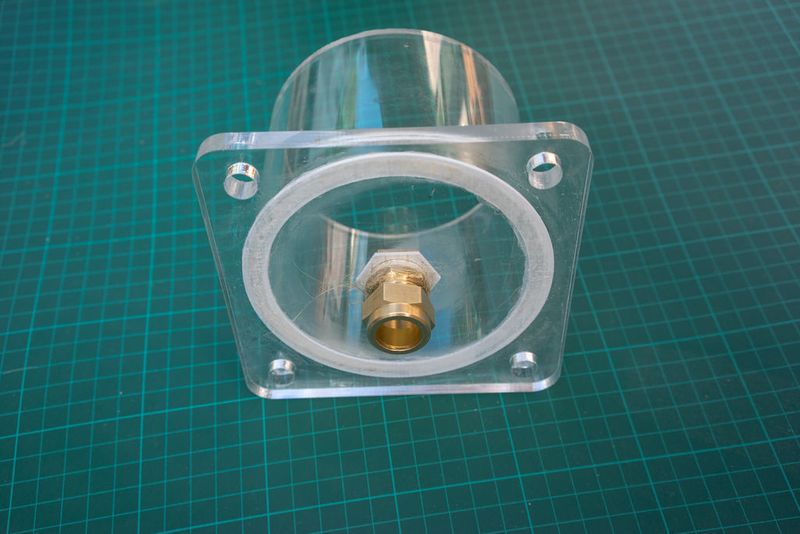
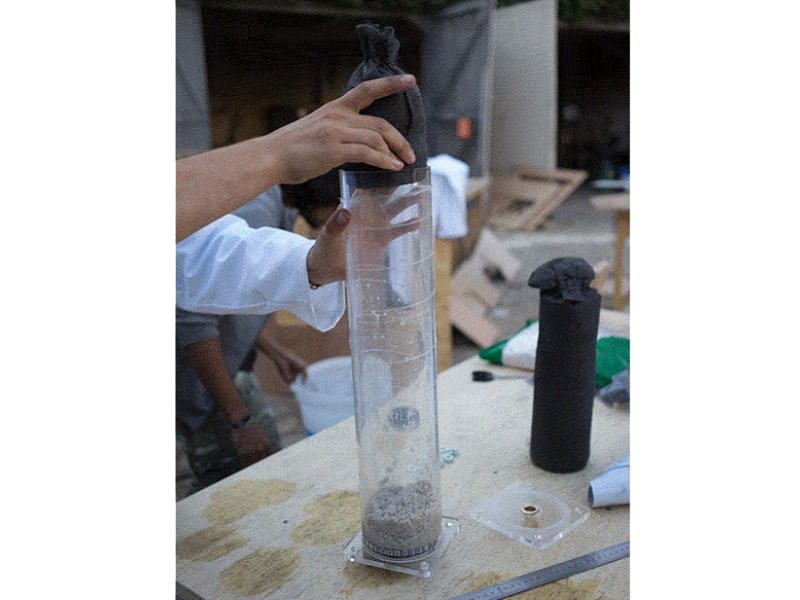
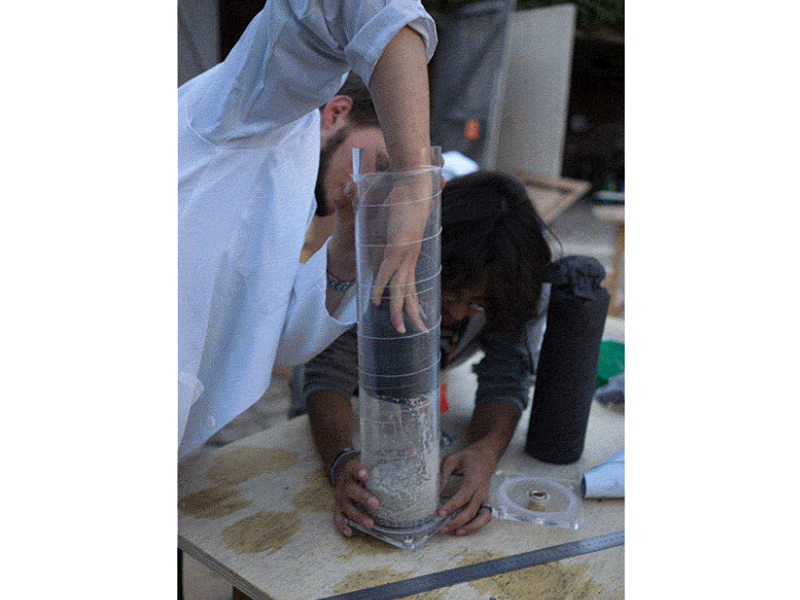
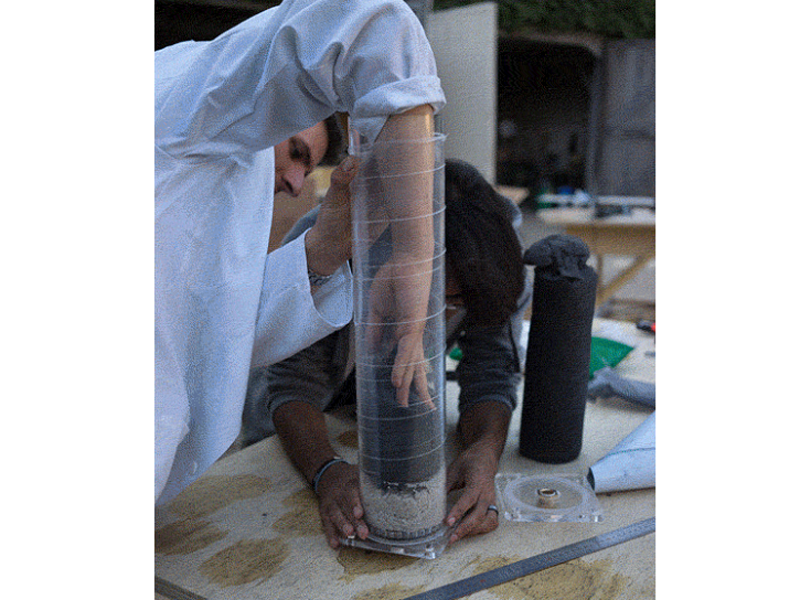
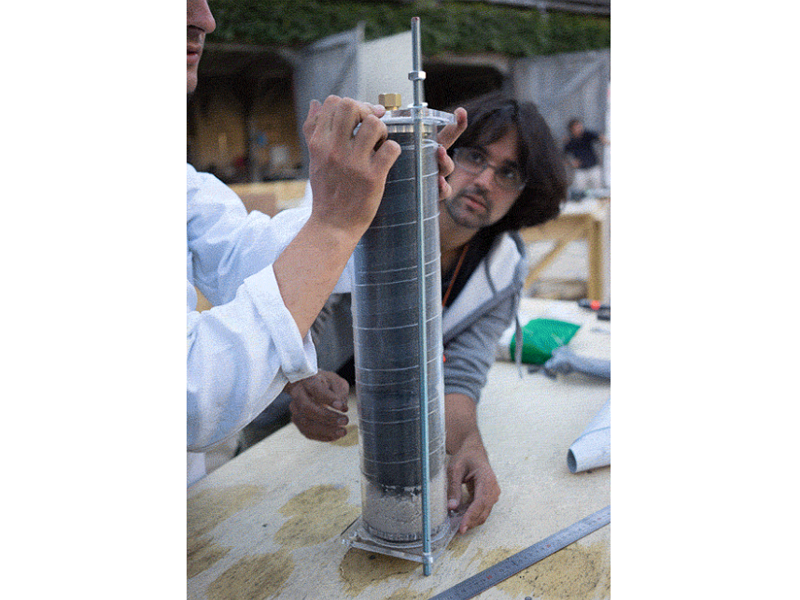
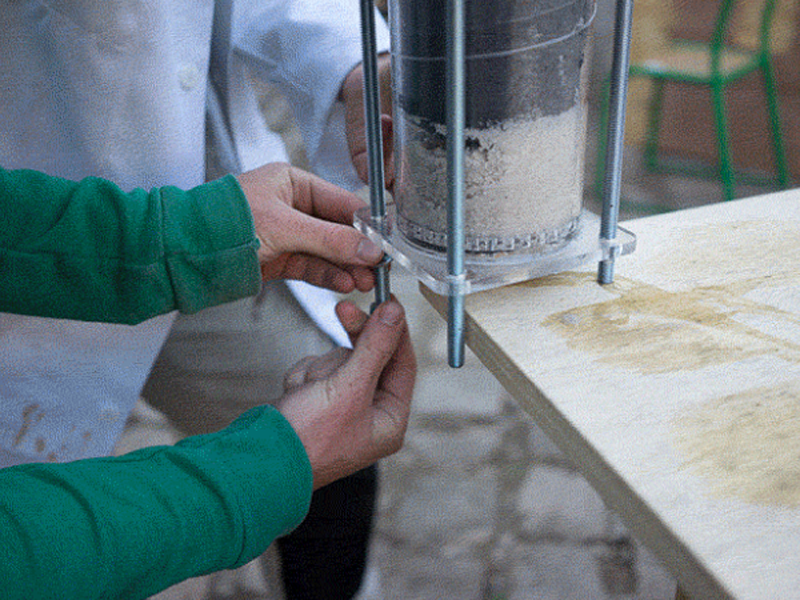
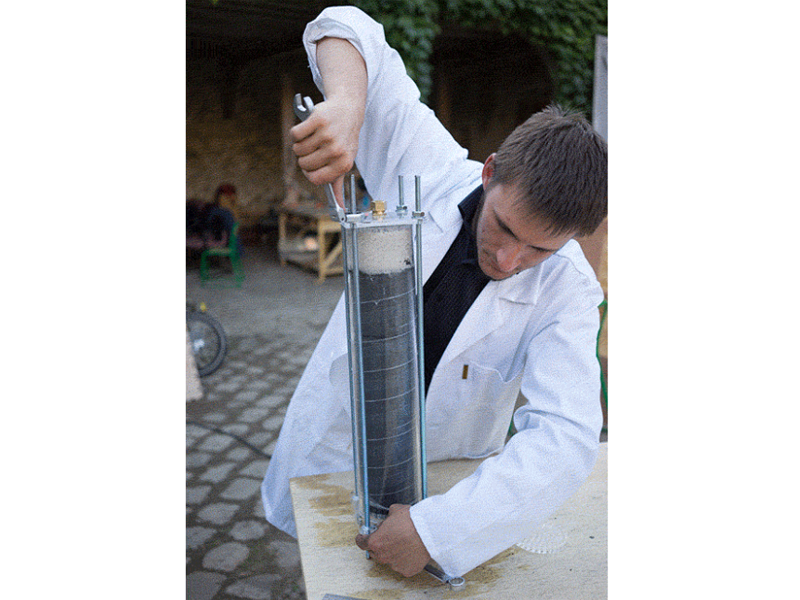
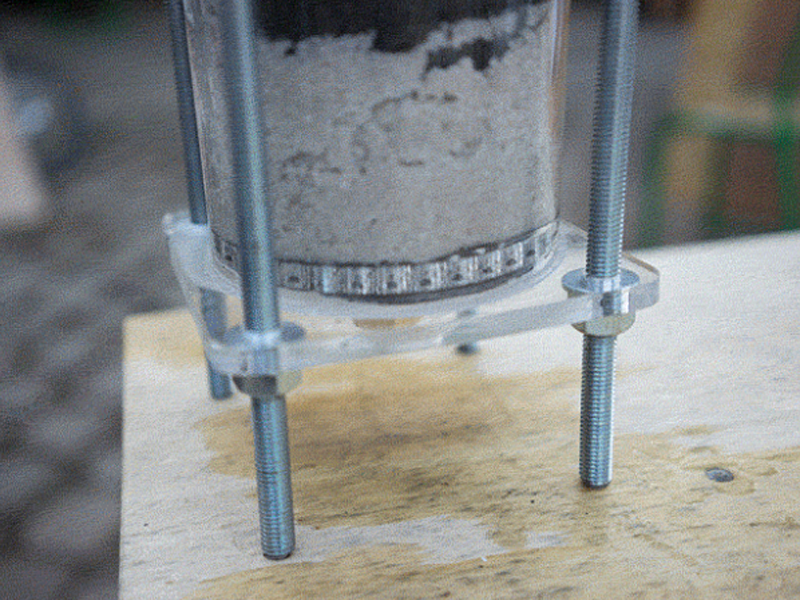
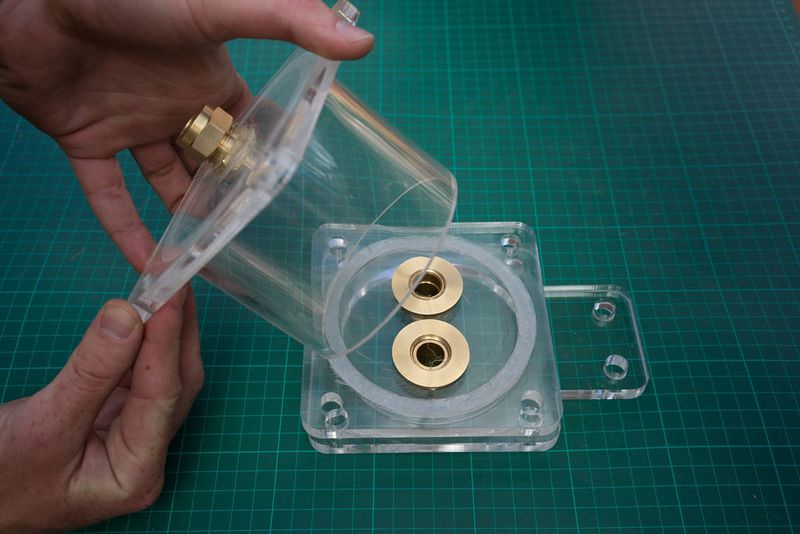
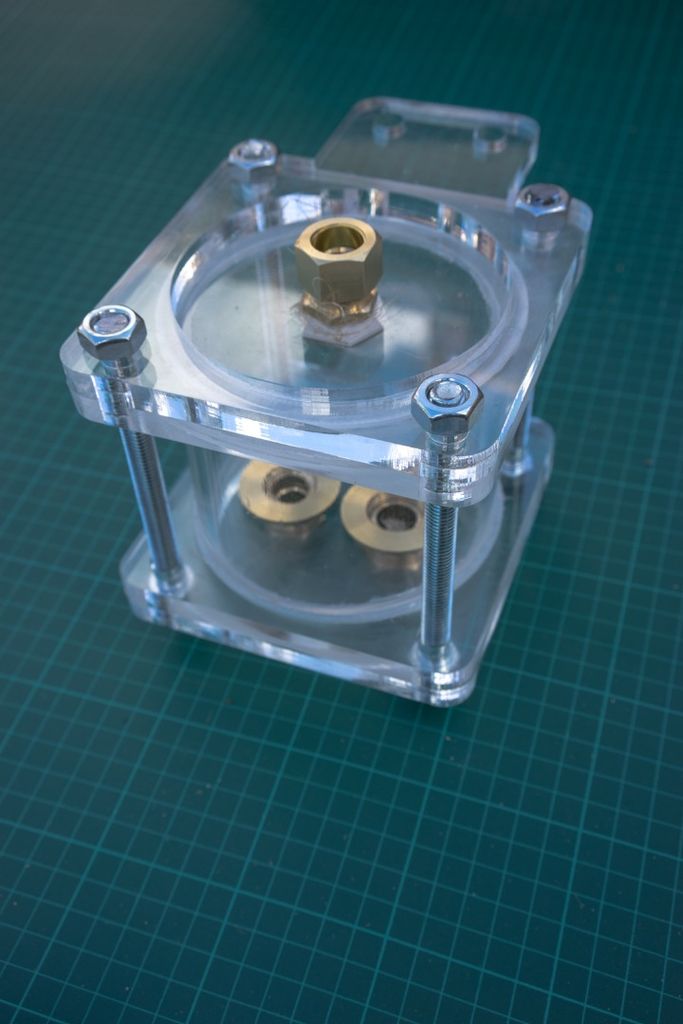
Étape 14 - Place the lid on a flat surface and add the pipe
Place the bottom lid on a flat surface and add the 50cm pipe on top. Clamp it to the table or have someone help you.
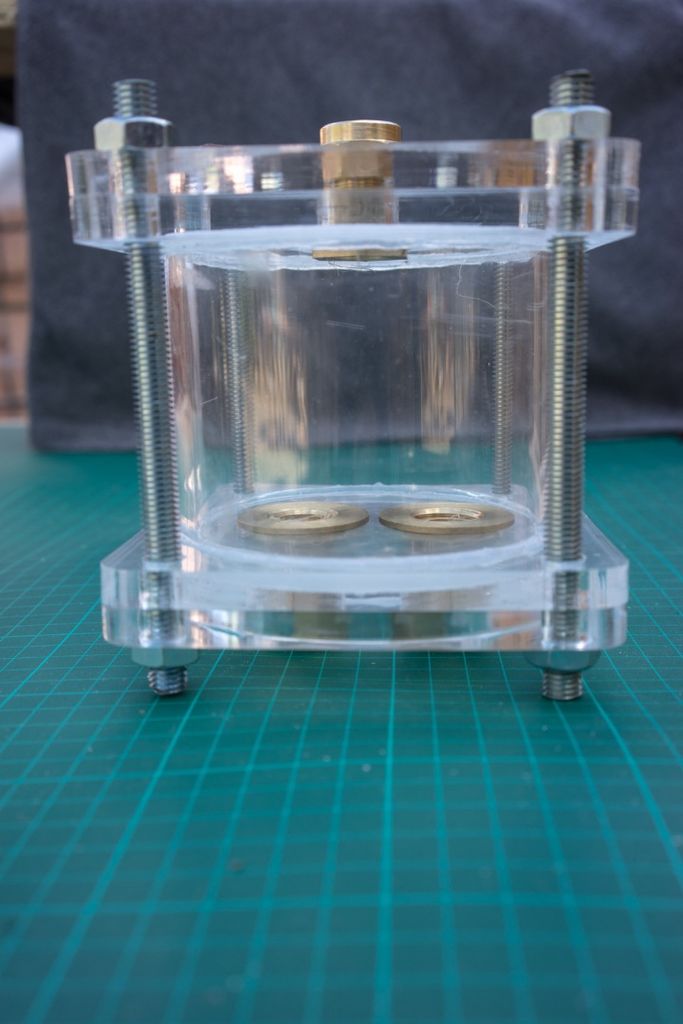
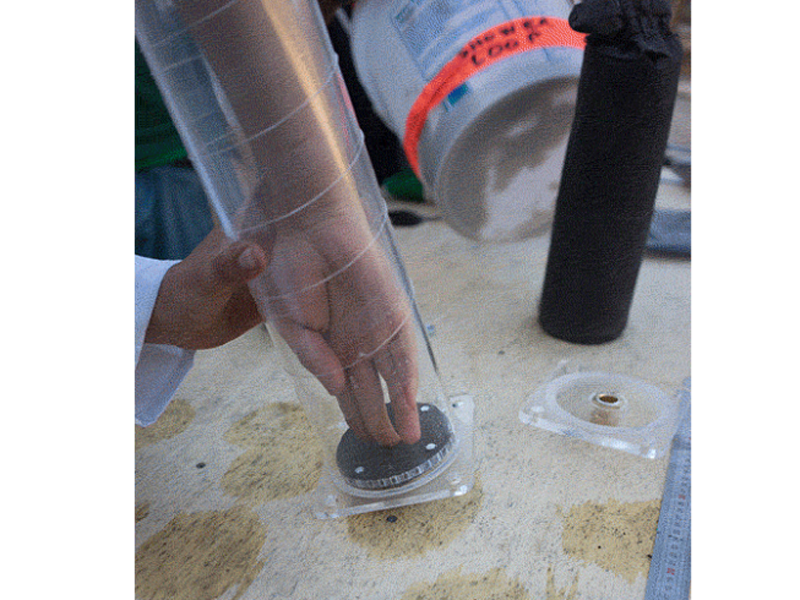
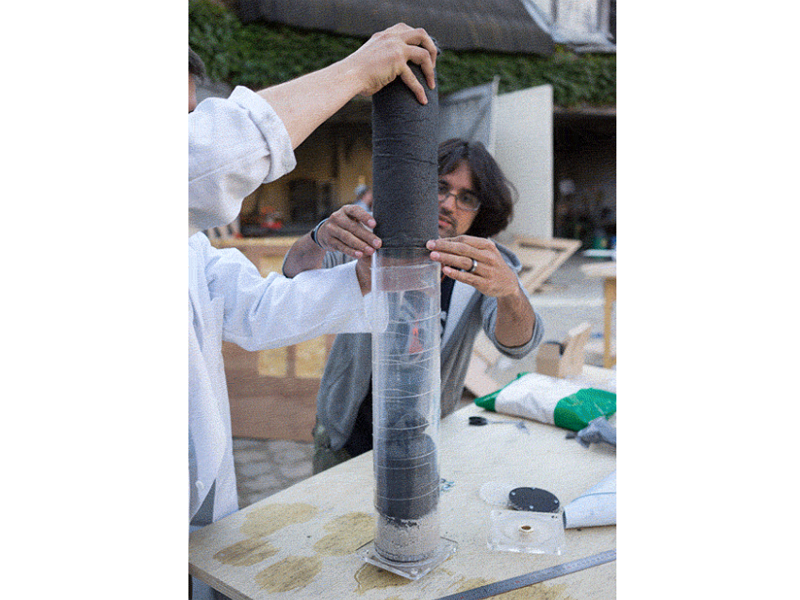
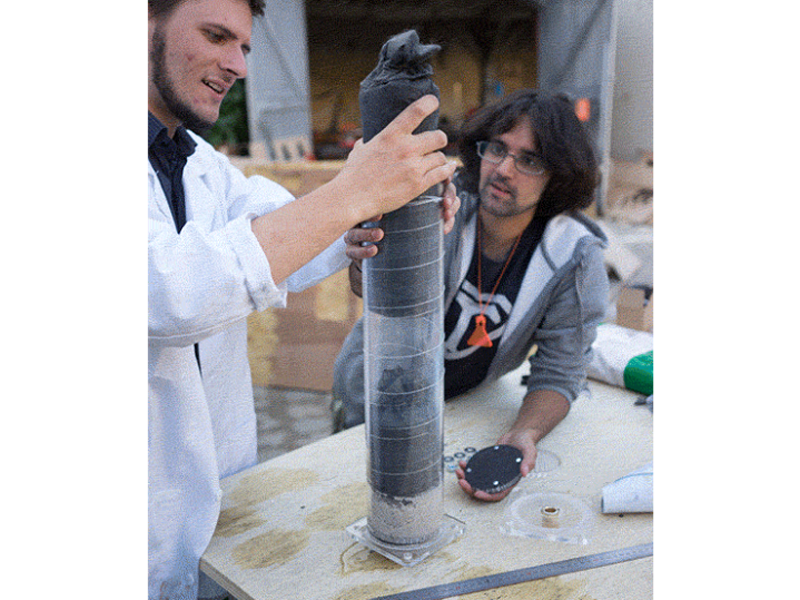
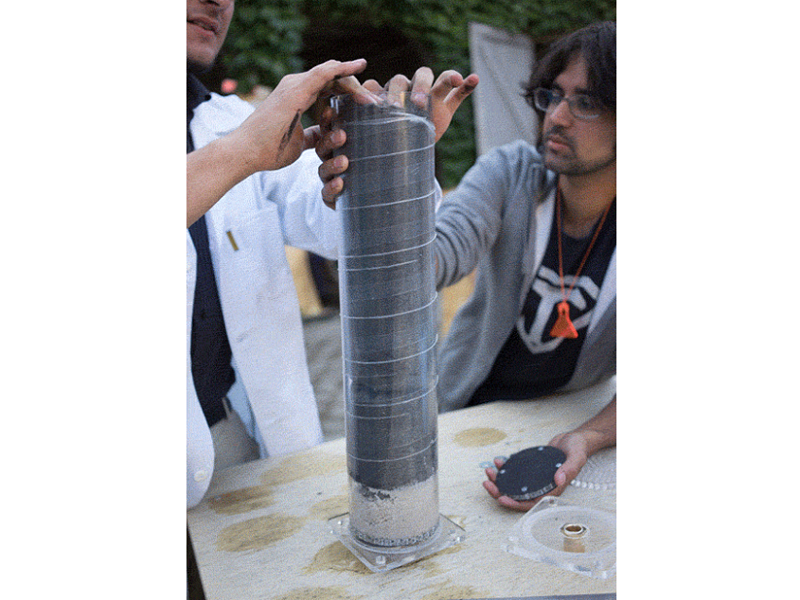
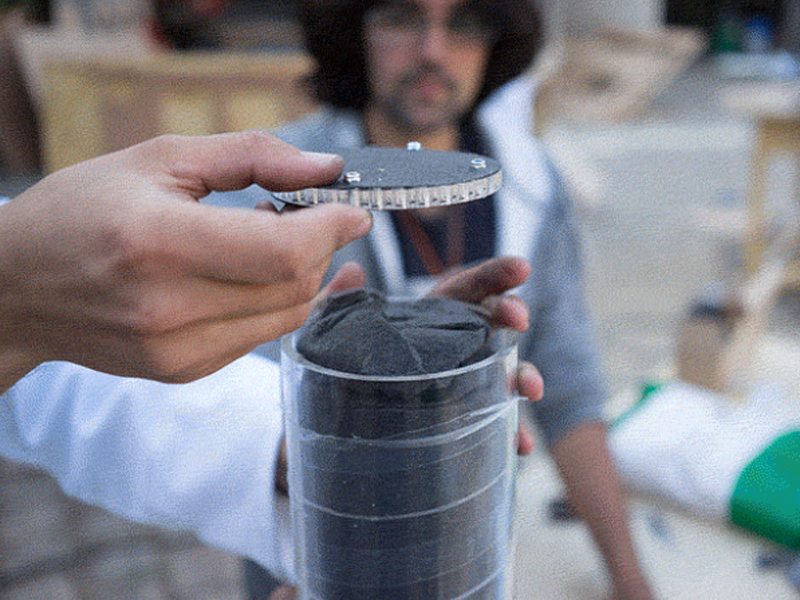
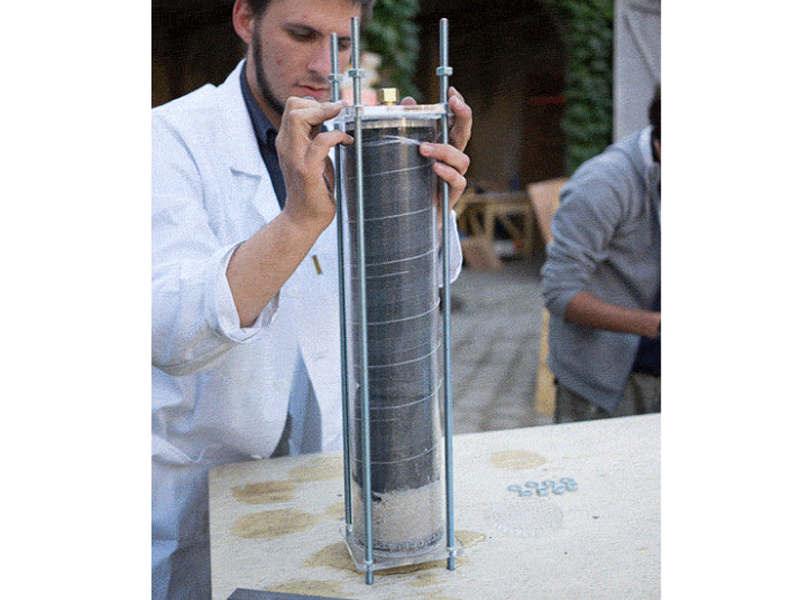
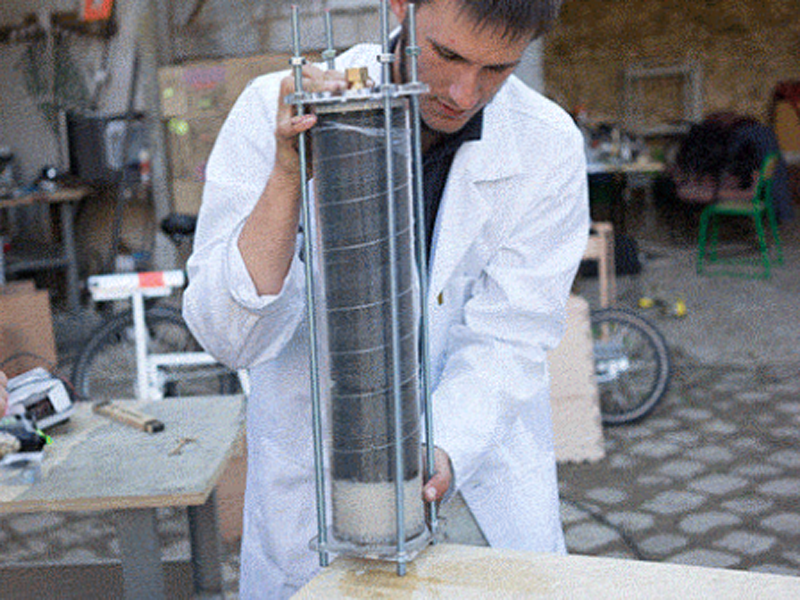
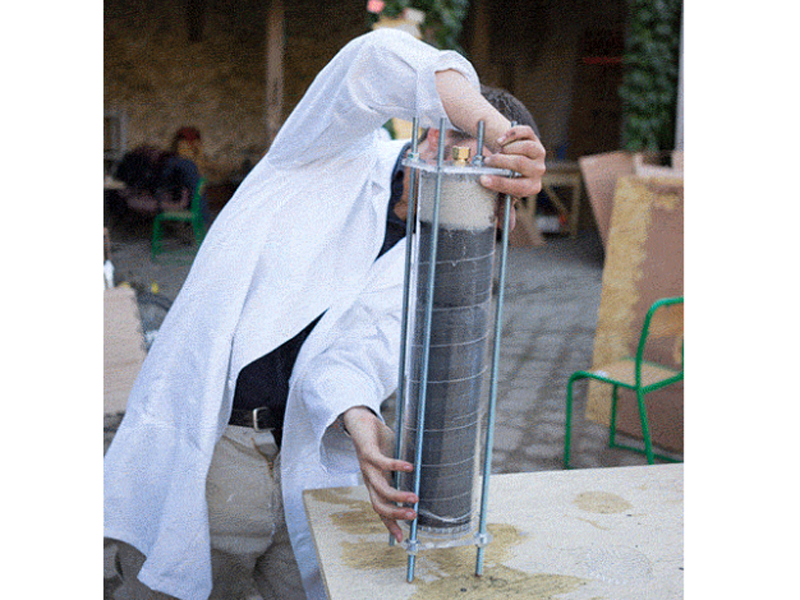
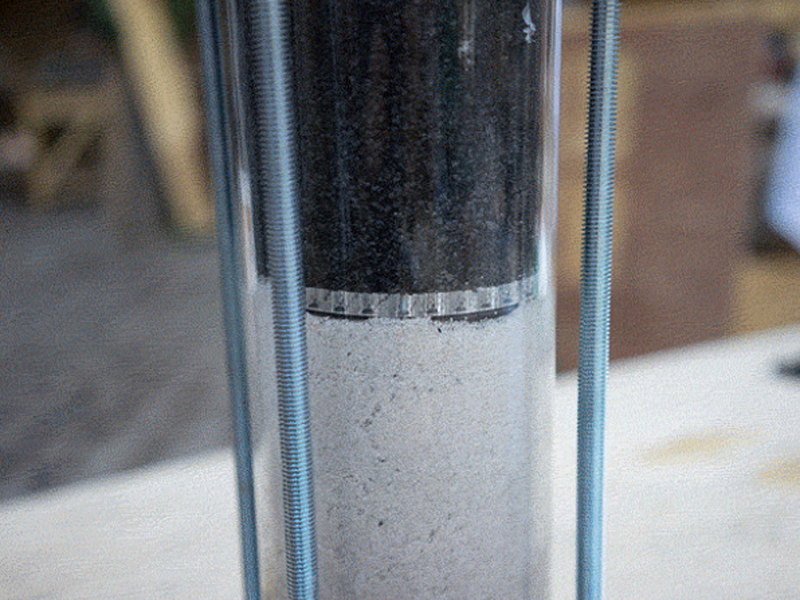
Insert the left over acrylic 'coins' from the laser cutting into the bottom lid (maybe glue them in). It's best to have two people for this step or use a clamp to hold the filter in place while adding the filtrates.
Étape 15 -
Insert the left over acrylic 'coins' from the laser cutting into the bottom lid (maybe glue them in). It's best to have two people for this step or use a clamp to hold the filter in place while adding the filtrates.
Published

































































 Français
Français English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Português
Português